Role Based Access Control
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) provides fine-grained control of user actions.
RBAC integrates with User Authentication, leveraging roles assigned to users in the credentials system of your choice. User roles are granted ALLOW, DENY, or STAGE to actions on specific resources.
RBAC configuration is defined in a YAML file and configured with an environment variable:
RBAC_CONFIGURATION_FILE=/path/to/rbac-config.yaml
Authorized roles
By default, Flex will restrict UI access to users who have at least one role defined in the RBAC configuration.
You may override this behaviour by providing a specific list of authorized_roles in your config.
You can open access to all users by specifying the special "*" role in the authorized_roles list.
Users who have an Admin Role assigned (see below) are considered authorized to access Flex regardless if authorization is derived from RBAC configuration or restricted to a specific list of authorized roles.
## Allow all users access to the UI ("*" is a role held by everyone)
authorized_roles:
- "*"
## Or, allow users with specific roles access to the UI
authorized_roles:
- "flex-user"
- "flex-admin"
- "ops-support"
Admin roles
You can optionally provide admin_roles, a list of roles considered to be admins in Flex.
You can learn more about administration in Flex here: Flex Admins.
admin_roles:
- "flex-admin"
Policies
An RBAC policy contains:
- Resource: The resource that this policy controls access to.
- Effect: Whether to deny, allow, or stage access to the Resource
- Actions: A list of actions that this policy Effects
Then either:
- Role: The user role that this policy applies to
- Roles: The list of user roles that this policy applies to
Example configuration
The following configuration describes policies for two roles, one of which is an admin role, and permits all authenticated users access.
Hint: Replace flex-admins and flex-users with role names from your Identity Provider.
authorized_roles:
- "*"
policies:
- resource: ["flink", "*"]
effect: "Allow"
actions: ["FLINK_SUBMIT", "FLINK_JAR_DELETE", "FLINK_JOB_EDIT", "FLINK_JOB_TERMINATE"]
role: "flex-admin"
- effect: "Allow"
actions: ["FLINK_JOB_EDIT"]
role: "flex-user"
resources: # resources (plural) is also supported:
- ["flink", "*", "flink-job", "PaymentStreamJob"]
- ["flink", "*", "flink-job", "ReconciliationJob"]
- resource: ["flink", "*", "flink-job", "PaymentStreamJob"]
effect: "Stage"
actions: ["FLINK_JOB_TERMINATE"]
roles: ["flex-user"]
flex-admin is allowed to upload, submit, edit and terminate all Flink jobs for all Flink clusters.
flex-user is only permitted to edit the Flink jobs: PaymentStreamJob and ReconciliationJob for all Flink clusters. flex-user can also stage the termination of the PaymentStreamJob - where a Flex admin will have to approve the termination request.
All remaining actions are implicitly denied actions to all users on all resources.
Resources
Resources are defined within a taxonomy that describes the hierarchy of objects in Flex.
[DOMAIN_TYPE, DOMAIN_ID, OBJECT_TYPE?, OBJECT_ID?]
Where:
- Domain Type: The top-level resource: flink is currently the only domain supported. Can be a wildcard (
*) to denote everything. - Domain ID: Unique identifier of the domain or
*. - Object Type: (Optional) Either flink-job or flink-jar.
- Object ID: (Optional) Unique identified of the object. Prefix and Suffix supported.
Specifying the object is optional. If not provided the resource includes all objects within a domain.
Example resources
["flink", "*"] - all flinks and all objects
["flink", "*", "flink-job"] - all topics on all flinks
["flink", "N9xnGujkR32eYxHICeaHuQ"] - all objects in a single flink cluster
["flink", "*", "flink-job", "csv-*"] - matching all flink jobs that start with `csv-`
Rules for using *
Flex supports a basic glob pattern, where wildcard (*) symbols are supported anywhere in the string:
| Scenario | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| All | * | All resources |
| Starts with | production-* | All resources starting with production- |
| Ends with | *-dlq | All resources ending with -dlq (dead letter queues) |
| Contains | -orders- | All resources containing -orders- |
| Middle wildcard | payments/*/events | Resources matching pattern with wildcard in middle |
| Multiple wildcards | prod--topic- | Resources with multiple wildcard positions |
| Namespace pattern | com.acme.*.events | Topics in any subdomain under com.acme and ending in the .events subdomain |
| Environment + service | staging-*-transactions | All transaction topics in staging environment |
Resource IDs
Flex logs the IDs of all top-level domains at startup.
Resource ID definitions
- Flink cluster: a SHA256 hash of the Schema Registry endpoint
Effects
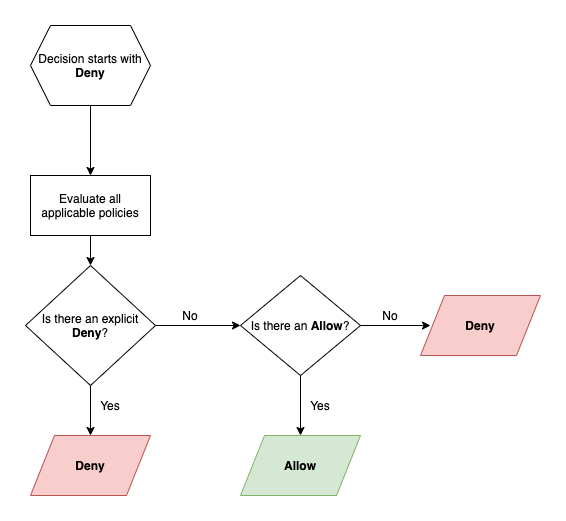
Note: Where multiple policies apply to one resource, Deny effects take precedence.
Specify Allow, Deny or Stage to indicate whether the policy allows or denies access to a resource. View Staged mutations documentation to learn about the Stage effect.
Where no matching policy exists the effect is an implicit deny.
Actions
See: User Actions.
Roles
Define a user role to which you would like to allow or deny access.
Can be a wildcard (*) to specify the policy is for all roles.
Role evaluation
User access to an action on a resource is determined by gathering all policies for roles assigned to a user and evaluating them with the following logic.
User access governance
All actions are retained in the Kpow Audit log. See: Data Governance (Audit Log).
Role mapping
To use RBAC you must configure User Authentication and ensure users have assigned roles.
Integration guides
Below are integration guides for common authentication providers:
OpenID
SAML
SAML integration (Generic)
Flex can integrate with your SAML IdP as a service provider.
Roles are defined in a Roles attribute in the SAMLResponse from your IdP.
If you would like to use a field other than the Roles attribute, you can extend the YAML configuration as follows:
saml:
role_field: "Groups"
Now, Flex will look to the Groups attribute for its basis of roles.