Groups
Prerequisites
- You have setup the correct access control permissions in Kpow to allow
GROUP_EDIT. See: User Authorization. - You have setup the correct Kafka ACLs if you have enabled ACLs in your Kafka cluster. See: Minimum ACL Permissions.
Group actions overview
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Reset offsets | Resetting group offsets by providing a new value or resetting them to a particular timestamp or a datetime |
| Clear offsets | Set the offsets to the earliest |
| Skip offsets | Incrementing the current offset. Can only be applied at the partition level |
| Remove member | Only if the consumer group is a static consumer group (a consupmer group with group.instance.id set) |
Group actions can be found in the navigation menu under the Consumers/Workflows section.
Select the consumer group you would like to manage from the dropdown, and you will see the consumer group topology.
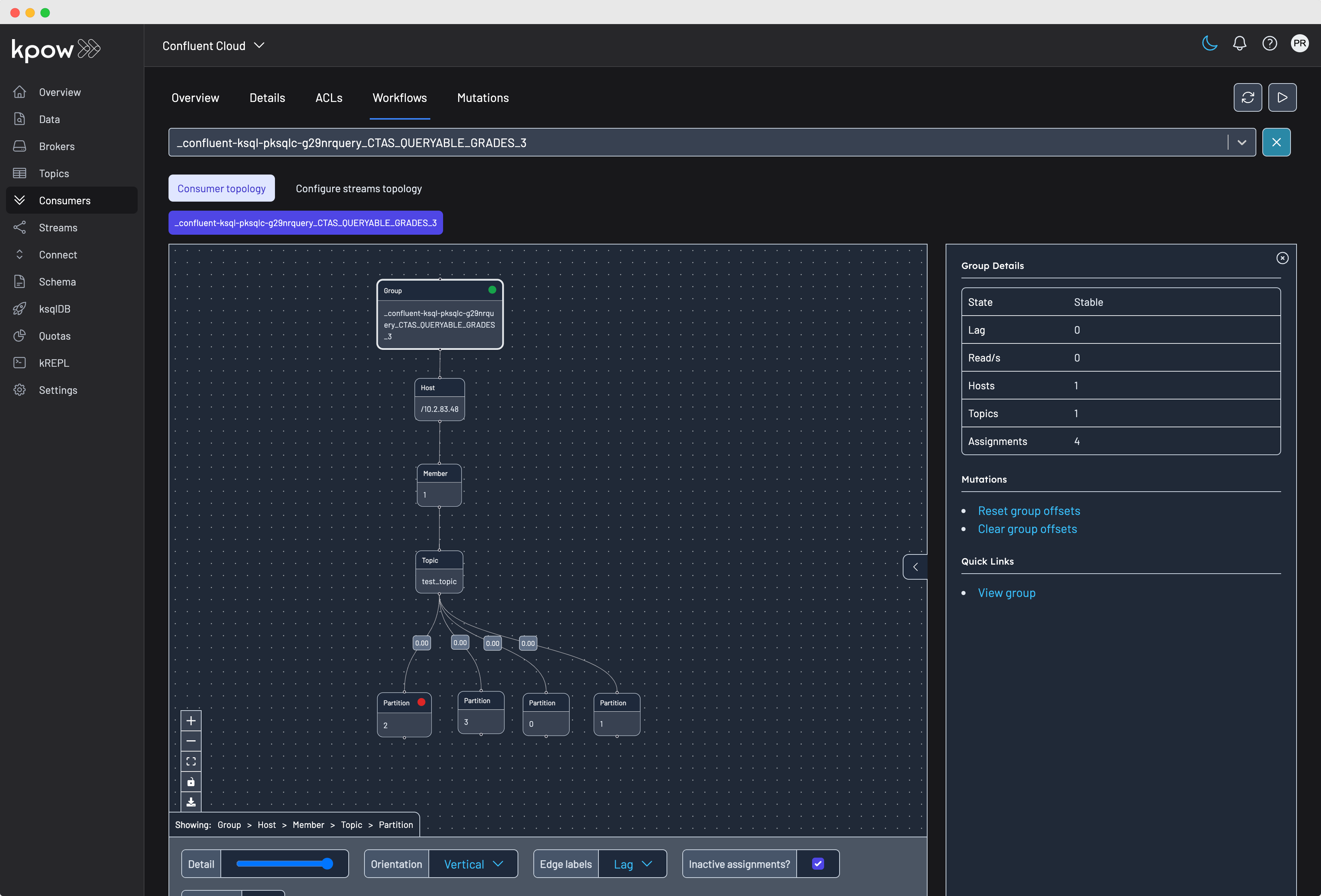
All offset management actions are available when clicking on a node:
Once you have selected a node, the available group offset actions can be found under the Mutations section on the right-hand pane.
Similarly, you can invoke the same mutations from the Consumer Details tab.
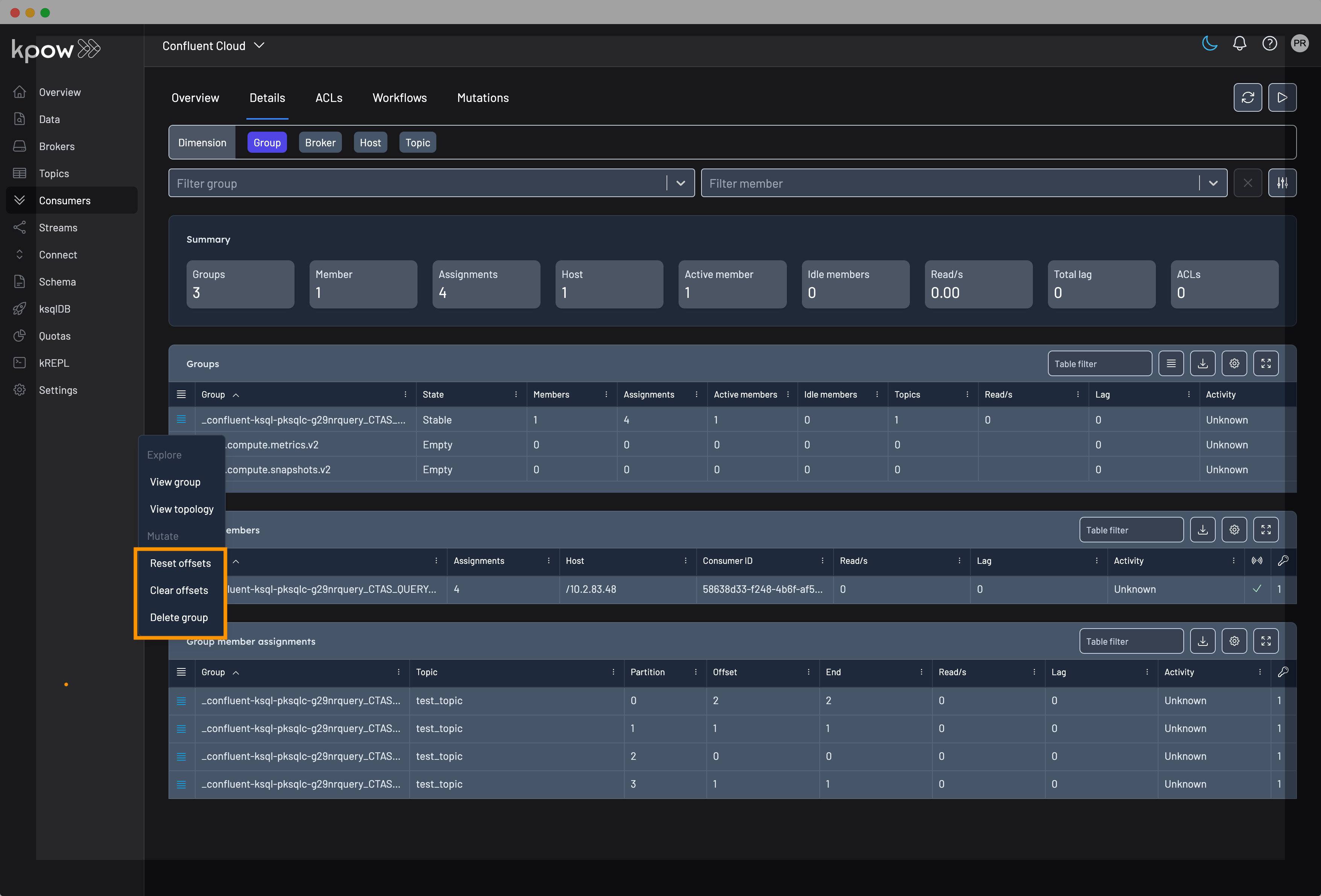
Offset actions
Rest offsets
Within Kpow you can change consumer group offsets from any dimension:
- Whole group assignments
- Host-level assignments
- Topic-level assignments
- Partition-level assignment
While resetting the offsets you can also choose the reset method.
- Offset
- Timestamp
- Datetime (Local)
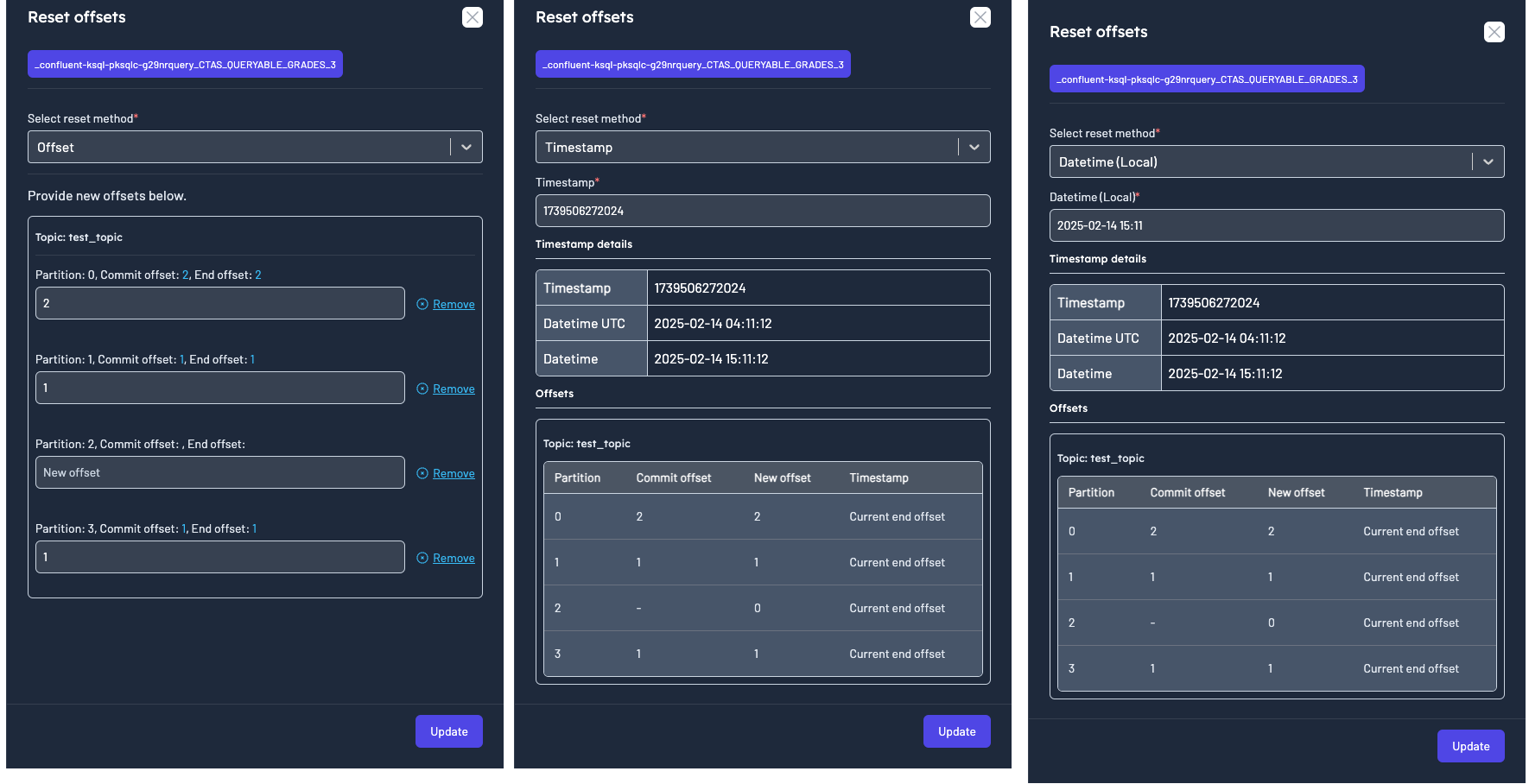
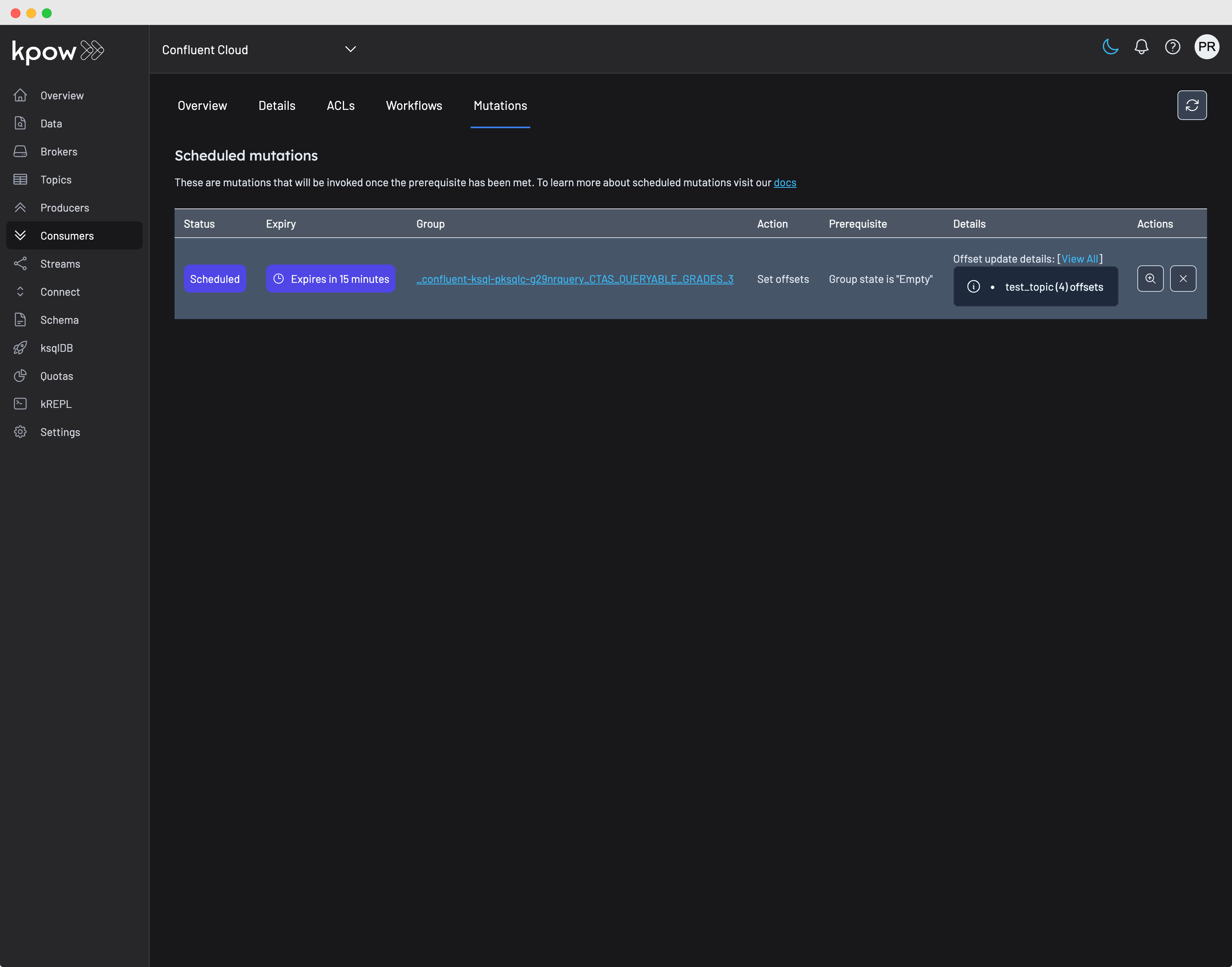
Scheduling a mutation
All group offset actions are scheduled, and will be invoked once all prerequisites have been met. For group offsets, the prerequisite is that the consumer group's state must be EMPTY. That is, you will have to manually scale down all instances of the consumer group to alter their offsets. This is because group actions cannot be performed on a running consumer group.
By default, Kpow will try to run the mutation for up to 15 minutes after it has been scheduled. You can cancel the mutation or view its current status by clicking on the Consumers/Mutations tab.
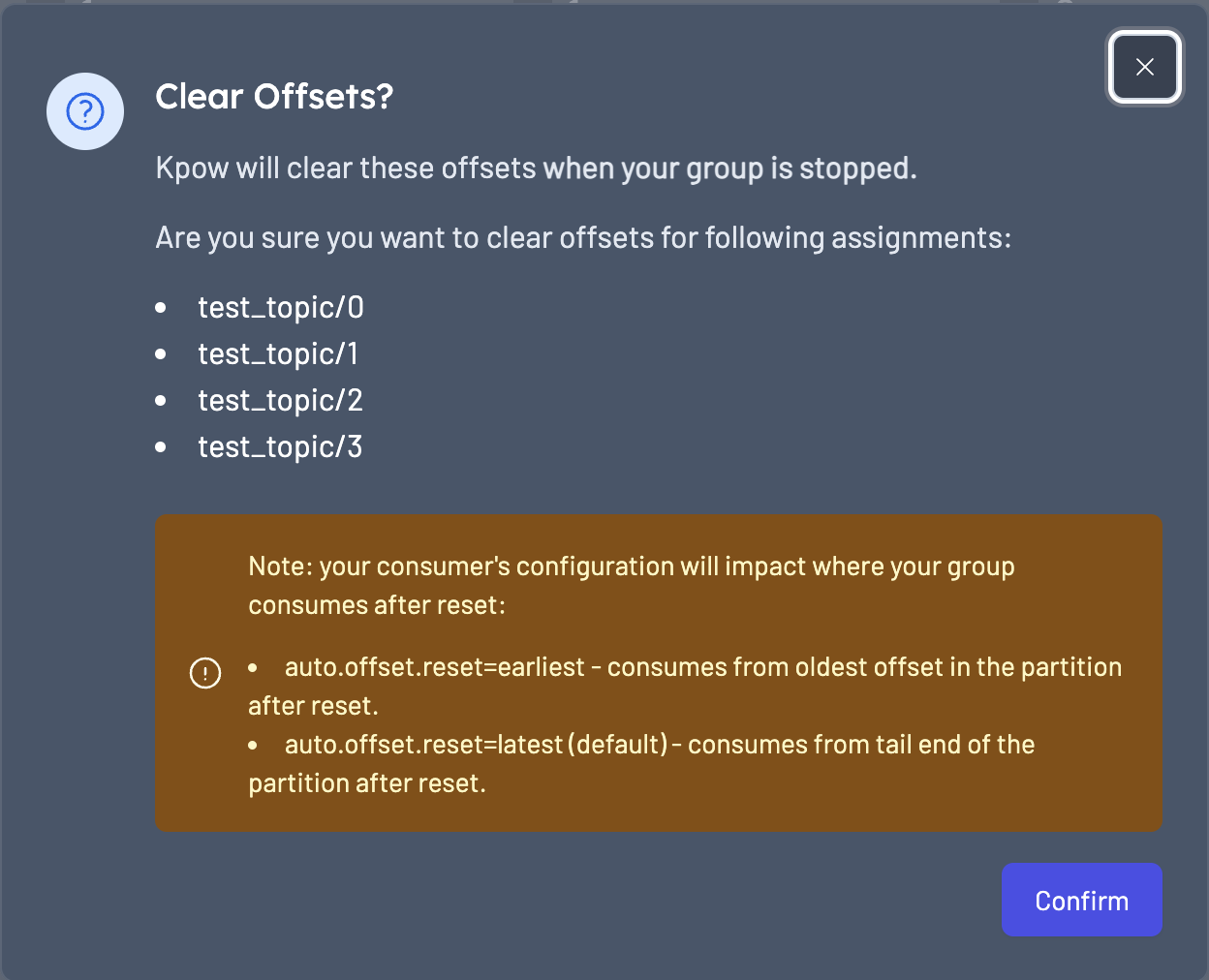
Clear offsets
This action will reset the offsets to the earliest. To clear offsets simply select the node from a workflow or in the table and click on 'Clear offsets' in the action menu.
Skip offset (partition level)
Increments the current offset by 1 for the partition assignment. To skip offsets select the partition node from a workflow or in the table and click on 'Skip offset' in the action menu.

Removing consumer group members
If you have a static consumer group (a consumer group with group.instance.id set) you can use Kpow to remove a member from the group. This can be useful as static consumer groups do not send a leave group request when they go offline, and instead rely on session.timeout to trigger a group rebalance.
When removing a member from a static consumer group it will have the effect of triggering a rebalance. This can be useful if you want to speed up the rebalancing process and don't wish to wait for the session.timeout value.
To remove a member from a consumer group navigate to the member in the consumer topology or table and click the "Remove Member" action. Removing members from a consumer group requires the GROUP_DELETE RBAC action.
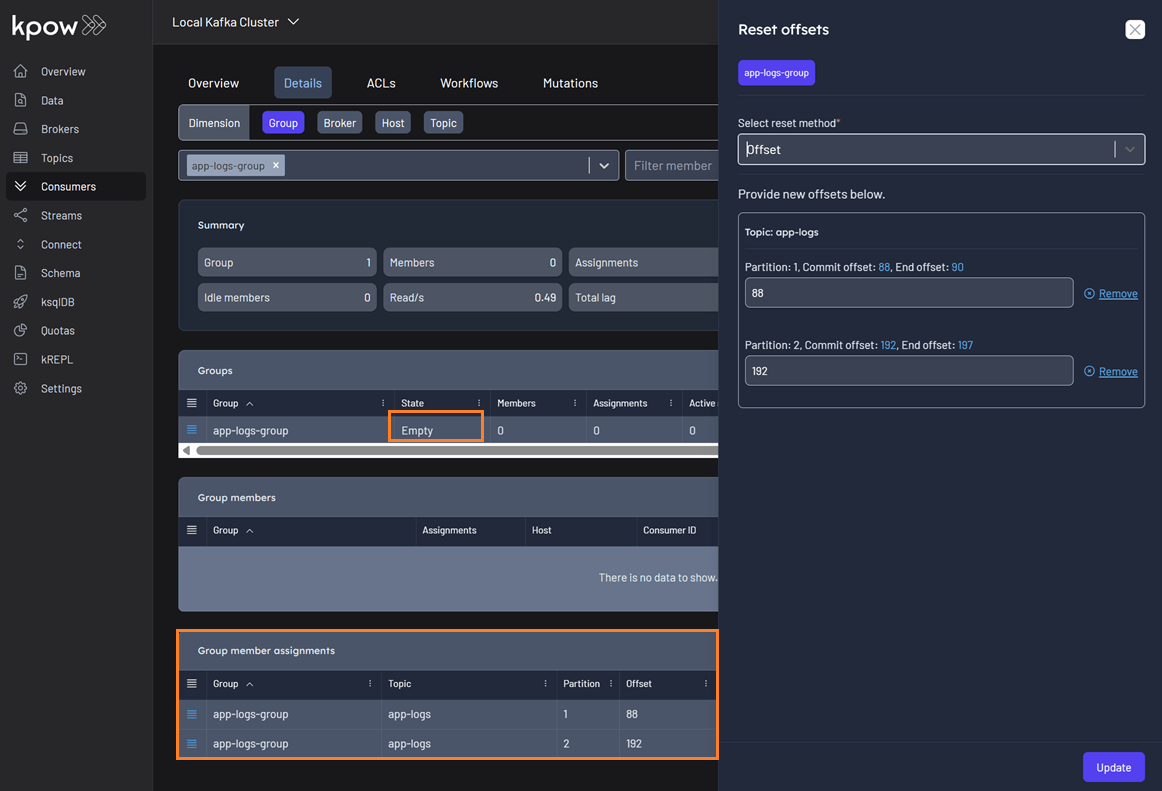
Empty group member assignments
Previously, EMPTY consumer groups showed no offset information in the reset offset UI, preventing customers from resetting their offsets. This was a critical issue when a poison message caused an entire consumer group to go offline. The fix now fetches offsets directly from the AdminClient instead of relying on the snapshot, ensuring offsets can be reset in these scenarios.
Simple consumers
What are simple consumers?
Kpow identifies a consumer group as simple if they are using manual partition assignment with no group coordination.
Simple consumers are identified using the isSimpleConsumerGroup() method from the GroupListing response, which is provided by the AdminClient/listGroups API call.
Some production workloads use this mechanism under the hood such as:
- Some Flink or Spark jobs (depending on version and connector)
- Older versions of Kafka Streams (pre–0.10.x)
- Some Python/Go Kafka clients default to this method of consumption
- Java applications using
.assign()instead of.subscribe()
Differences
Simple consumers operate differently from standard consumer groups:
Standard consumer groups use Kafka's group coordination protocol where a broker acts as coordinator, managing member lifecycles, partition assignments, and rebalancing. These groups have states (like Stable, Rebalancing, Empty) and track which consumer instances are assigned to which partitions.
Simple consumers bypass this coordination entirely. They:
- Manually assign partitions without broker coordination
- Have no group state or rebalance protocol
- Don't report member/host assignment information
- Only use Kafka to store offset commits (optional)
- Manage their own partition assignment logic
This means simple consumers have more control over consumption but require manual intervention for operations like offset resets - in most cases, changes won’t take effect until the consumer restarts or explicitly re-seeks offsets.
Because simple consumers contain less metadata, they are presented in their own top-level tab in the Consumers UI named 'Simple consumers'. This tab will only be visible in Kpow if the selected cluster has simple groups running.
Simple consumer management
Kpow's Simple consumers UI offers the same offset management options as regular consumer groups in Kpow.
However, there are some key differences in behaviour:
- There is no scheduling of simple consumer groups because there is no 'Empty' state prerequiste required to alter a simple consumers offsets
- Offsets are updated immediately in Kafka’s offset store, but Kafka does not notify active simple consumers of this change
Therefore, we recommend scaling down your simple consumers to zero instances before resetting offsets.