ksqlDB
Kpow offers a robust and user-friendly interface for managing your ksqlDB clusters, providing capabilities for source and query management, SQL execution, and record insertion.
All management functions are fully integrated with Kpow's enterprise features, ensuring that your streaming data platform is both powerful and secure.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Kpow enforces fine-grained permissions for all ksqlDB interactions. Actions like
KSQLDB_QUERY,KSQLDB_EXECUTEorKSQLDB_TERMINATE_QUERYallow administrators to precisely control which users can read data, create new streams or tables, or terminate running queries. Policies can be applied to specific ksqlDB clusters, providing granular control over your environment. - Multi-Tenancy: Kpow's tenancy model extends to ksqlDB, allowing you to create isolated environments for different teams or projects. This ensures that users within a specific tenant can only view and manage the ksqlDB resources allocated to them, preventing unauthorized access and interference across teams.
- Data Governance and Audit: Kpow enhances data governance by providing a complete audit trail. Every action performed through the UI—from executing a
SELECTquery to creating a table or terminating a query—is captured in Kpow's audit log. This provides full visibility into user activity, ensuring compliance and accountability.
Prerequisites
To effectively use Kpow for ksqlDB management, you must first ensure that your environment is correctly configured and that users have been granted the necessary permissions.
- You have configured ksqlDB and Schema Registry within your Kpow environment. While Schema Registry is optional, its configuration is highly recommended for sources that use Avro, Protobuf, or JSON Schema.
- You have set up the correct permissions for users. All actions within the ksqlDB UI, from viewing data to creating tables or terminating queries, are governed by Kpow's access control system. For more information, see User Authorization.
Source management
In ksqlDB, sources are the streams and tables that form the building blocks of your stream processing applications. Kpow provides a comprehensive suite of tools to explore and manage these sources directly within its user interface, combining ksqlDB's power with Kpow's enterprise features like RBAC and schema integration.
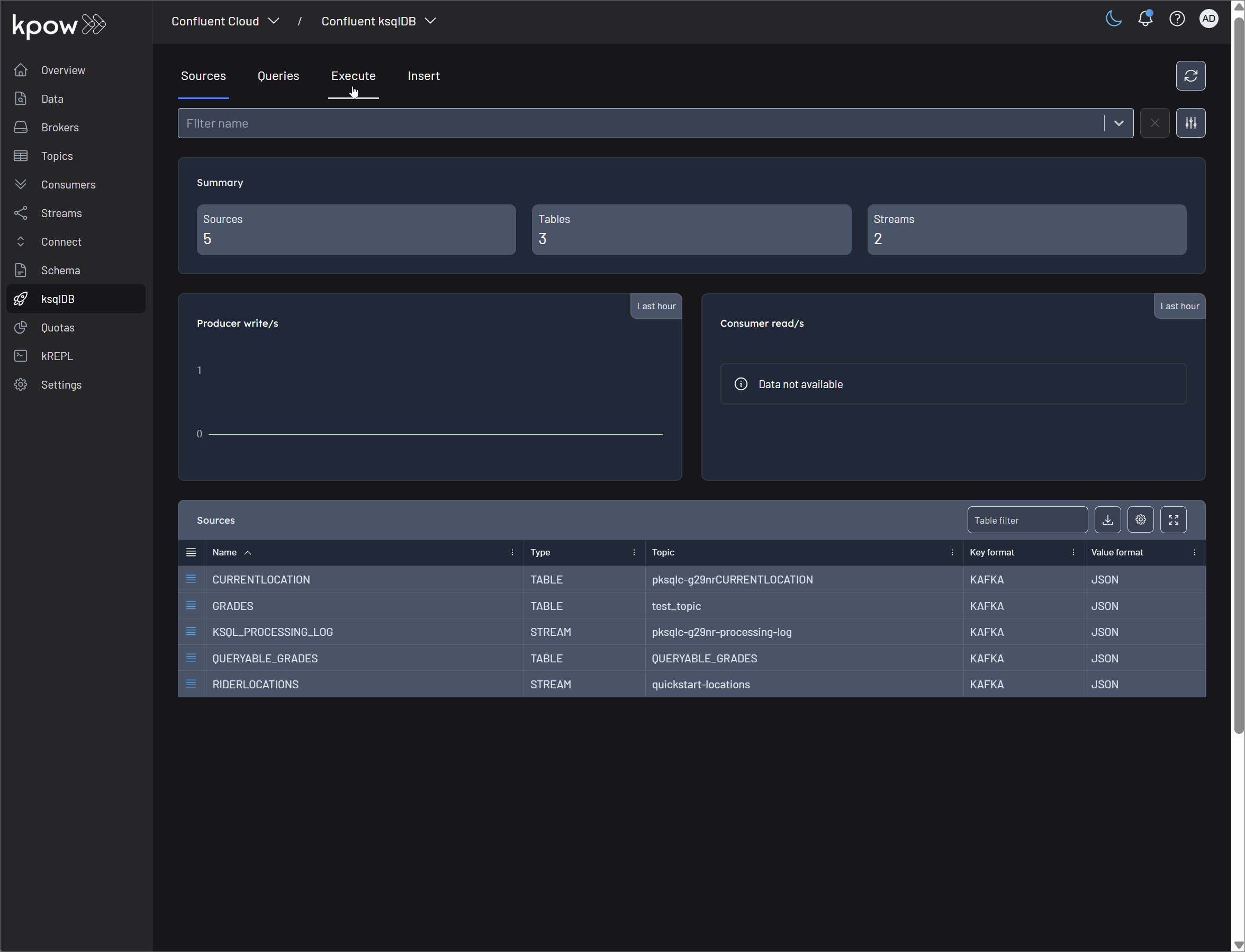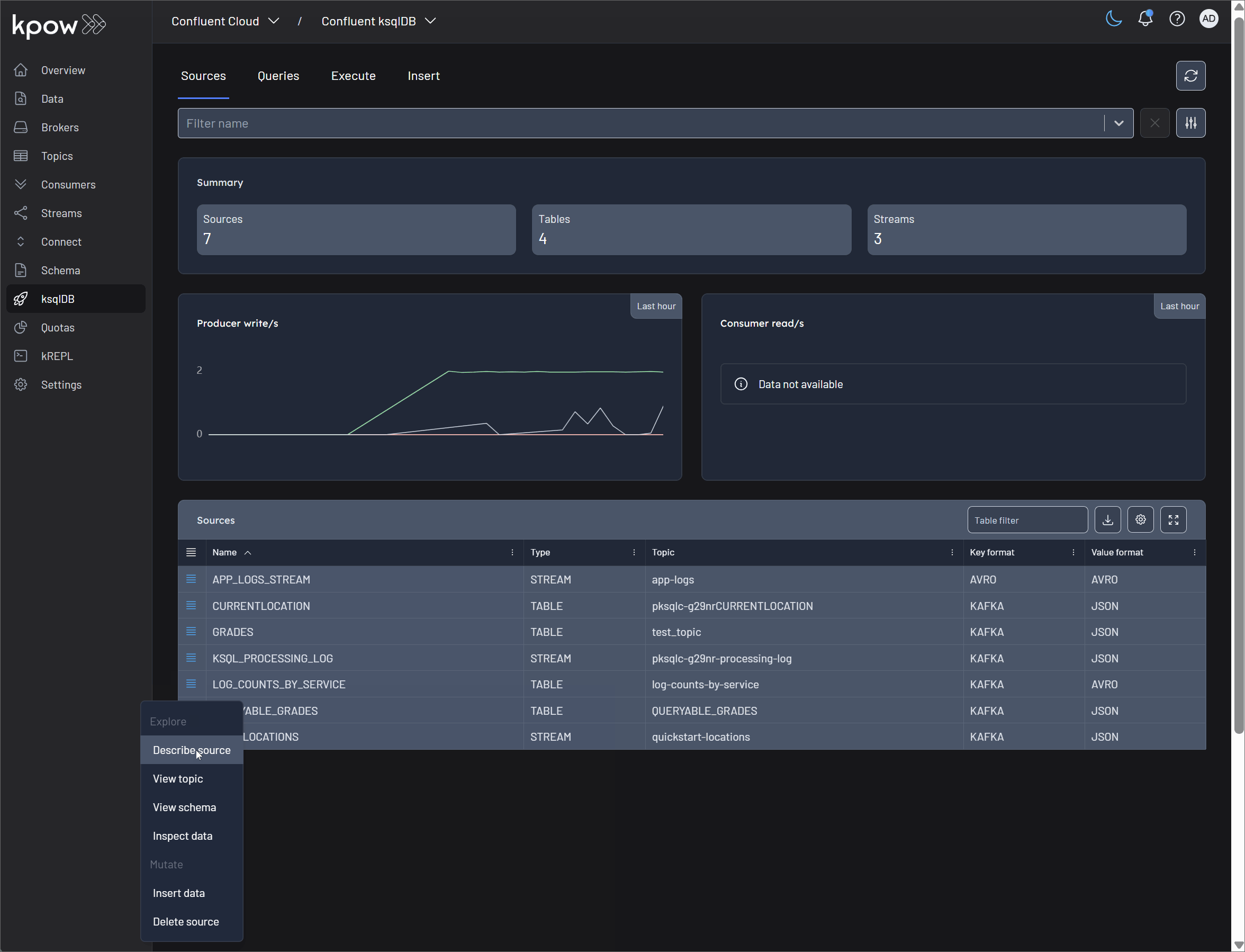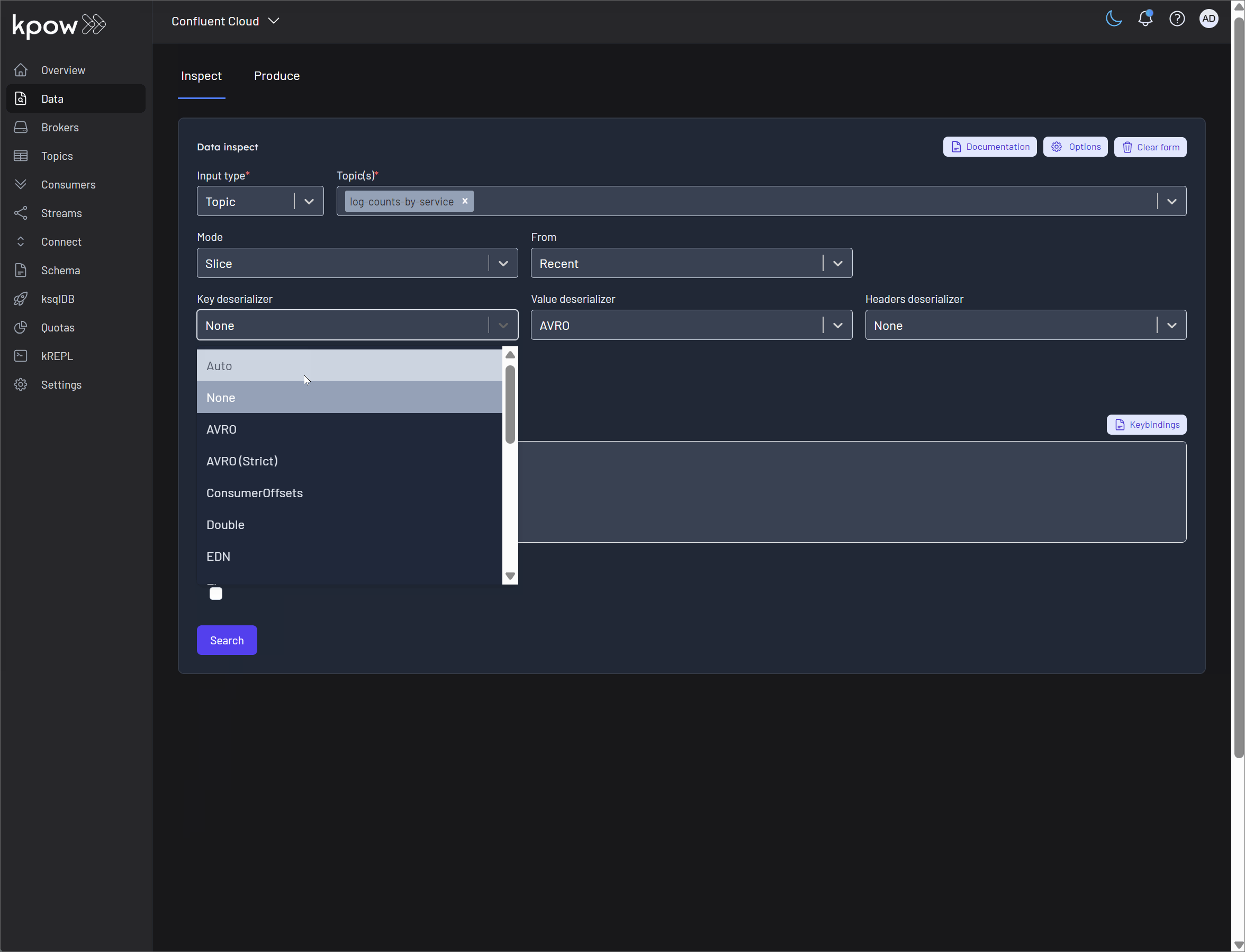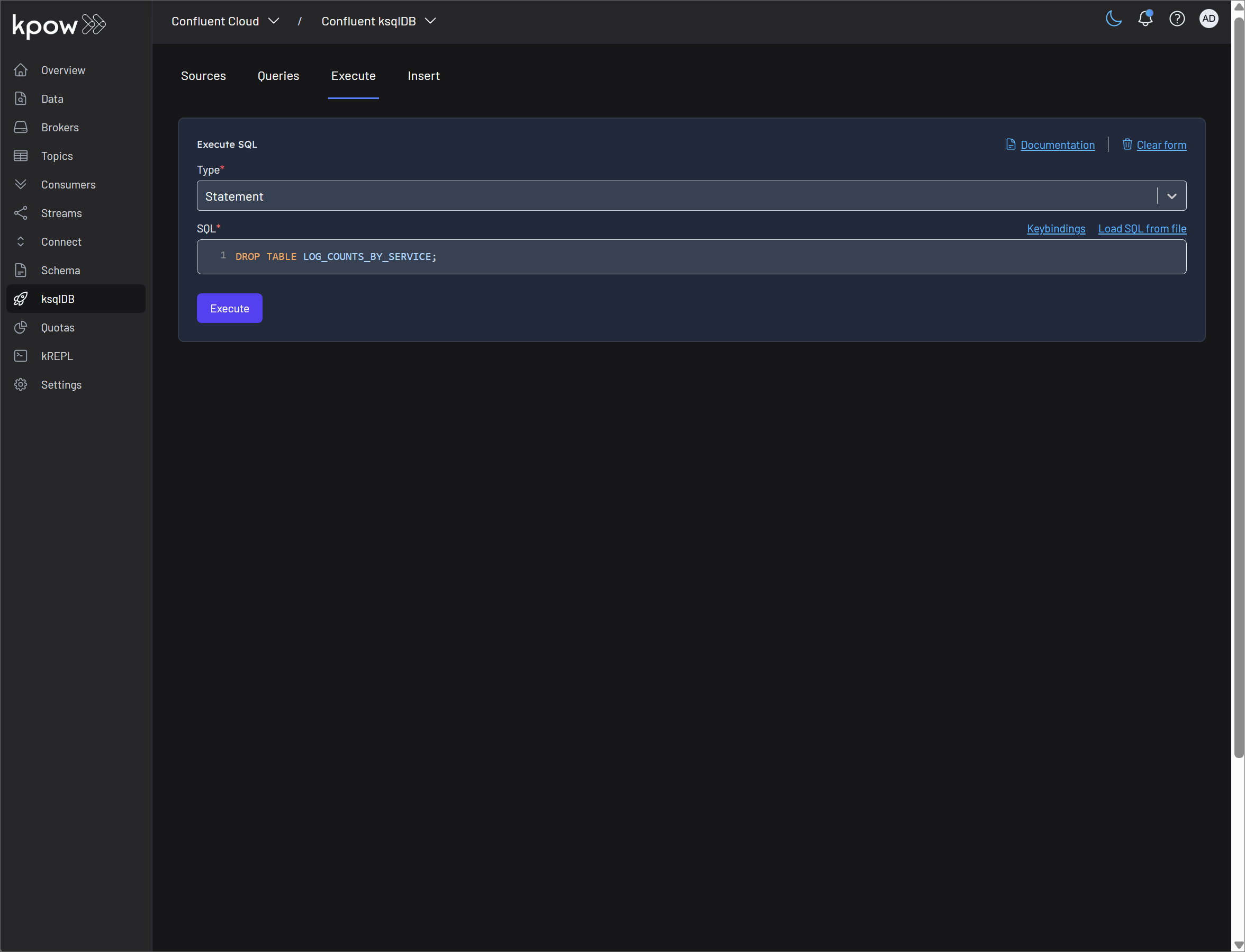
Explore Options
These features allow you to inspect and understand your ksqlDB sources without altering them.
-
Describe Source: This is your primary view for understanding a ksqlDB source at a glance. It provides a detailed breakdown, including:
- Metadata: Core characteristics of the source, such as its
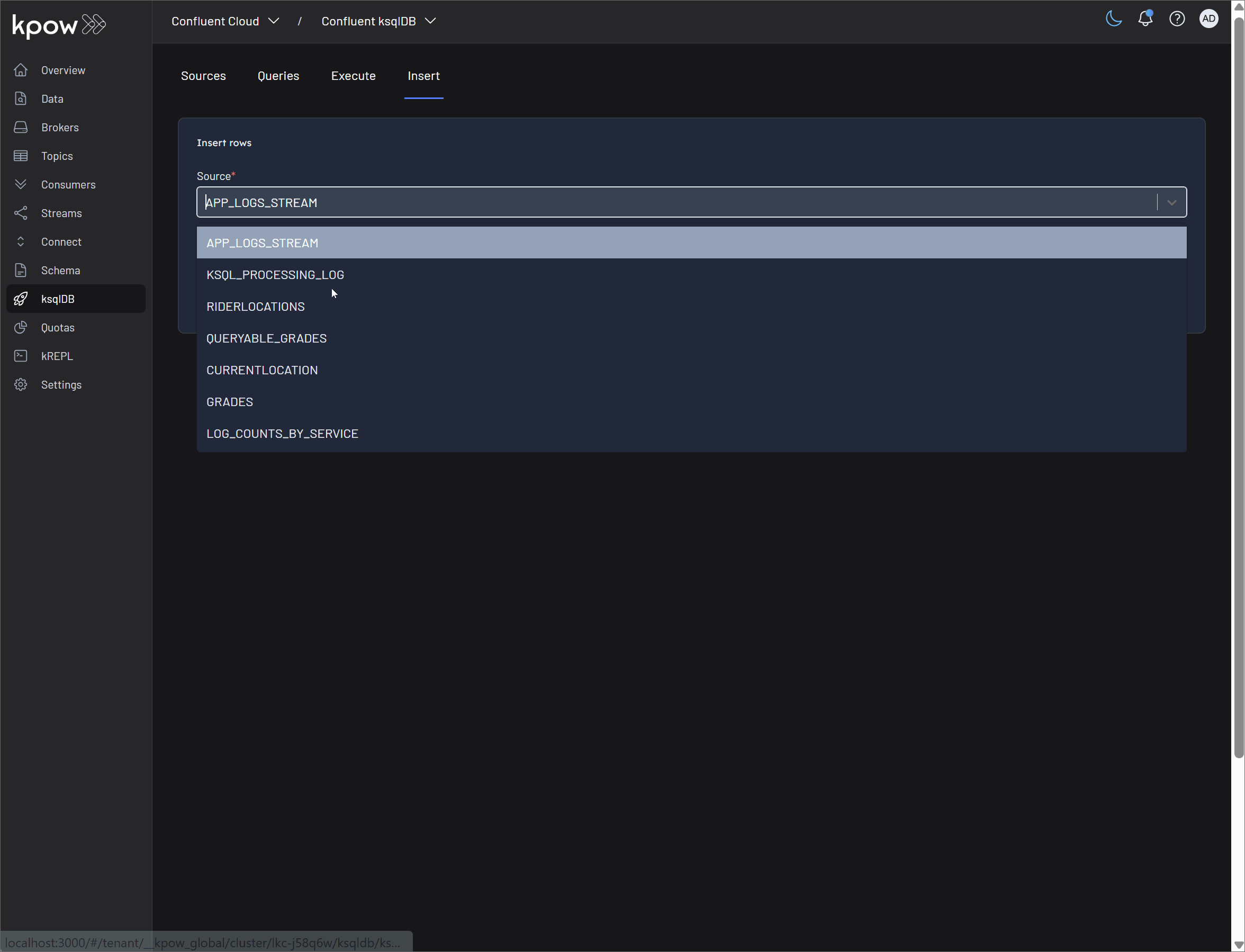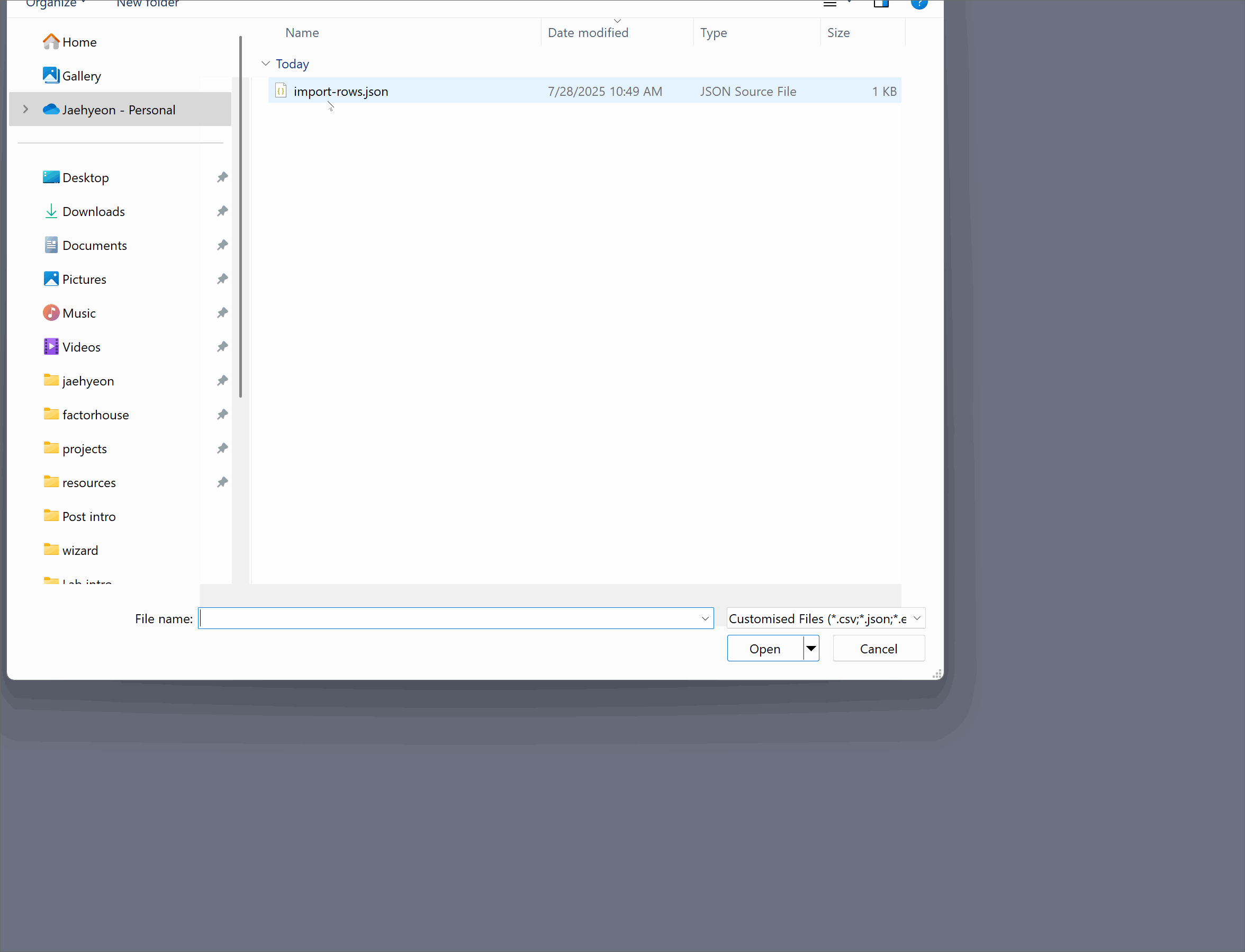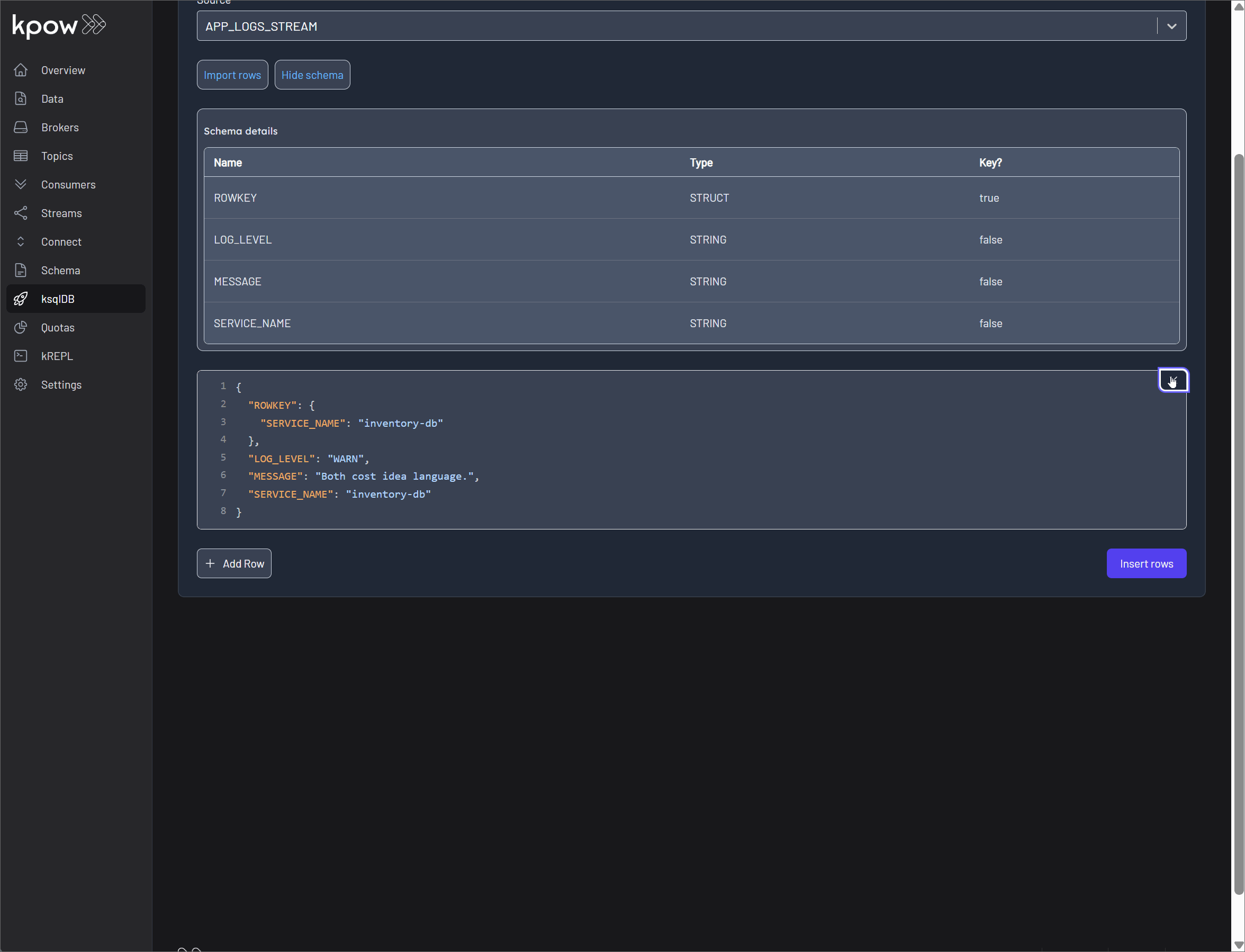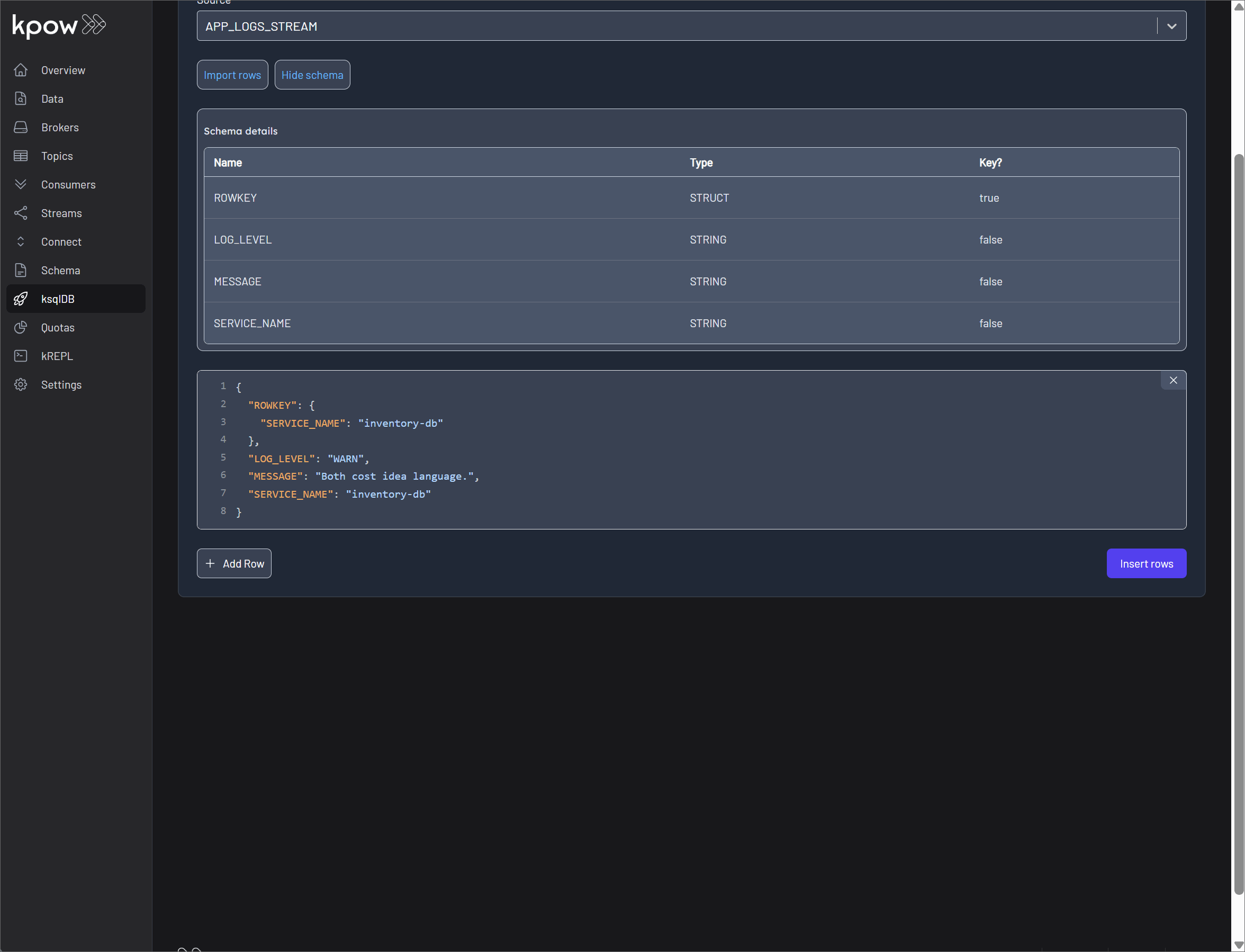
Type(STREAM or TABLE), the underlying backingTopic, the dataFormat(e.g., AVRO, JSON), and timestamp and windowing details. - Fields: The schema of the source, listing each column's
Name,Type, and whether it serves as a primaryKey. - SQL: The exact
CREATEstatement used to generate the stream or table. This is invaluable for understanding its origin, dependencies, and configuration. - Key/Value Schema: The raw Avro, Protobuf, or JSON schema definition for the source's key/value.
- Read/Write Queries: Kpow provides a complete data lineage view by listing all persistent queries that interact with a given source. This section shows the queries that read from the source (i.e., use it as an input in a
FROMclause) as well as the queries that write to it (i.e., target it as aSINK). This gives you a comprehensive understanding of a source's upstream and downstream dependencies, including the query ID, its sink, and the full SQL statement for each interaction.
- Metadata: Core characteristics of the source, such as its
-
View Topic: This option provides a direct link to Kpow's detailed view of the underlying Kafka topic that backs the stream or table. From here, you can inspect topic-level configurations, partition information, and other critical Kafka metrics.
-
View Schema: Kpow integrates seamlessly with your Schema Registry. This allows you to click through to view the detailed schema associated with your source's value (and key, if applicable). You can see the full schema definition, its version history, and compatibility settings.
-
Inspect Data: This powerful feature leverages Kpow's Data Inspect capability to let you view the actual messages within the source's underlying Kafka topic. It's an essential tool for debugging, allowing you to see the raw data as it flows through your system, rendered with the appropriate schema.
Mutate Options
These actions allow you to modify your ksqlDB sources or the data within them.
-
Insert Data: Kpow provides a user-friendly UI to produce new records directly into a ksqlDB source. This interface is ideal for testing, back-filling data, or making manual corrections. See Record insertion for details.
-
Delete Source: You can drop a stream or a table from the Kpow UI. ksqlDB requires that you first terminate any queries or drop any other sources that depend on it (e.g., a table that reads from a stream).
Query management
Persistent queries are the heart of a ksqlDB application, continuously processing data as it arrives. Kpow provides essential tools for monitoring the health and output of these queries, as well as the control to manage their lifecycle.
Explore Options
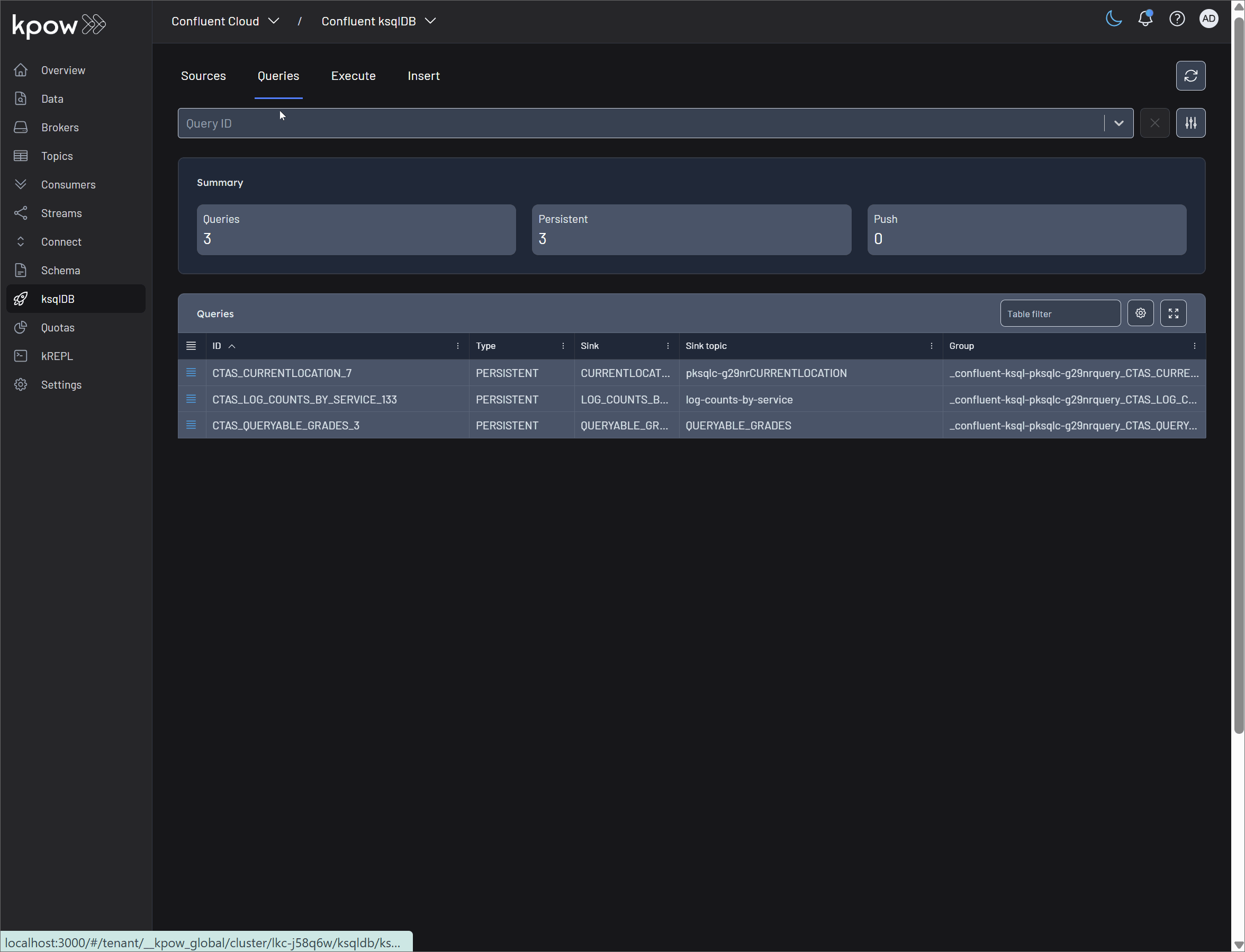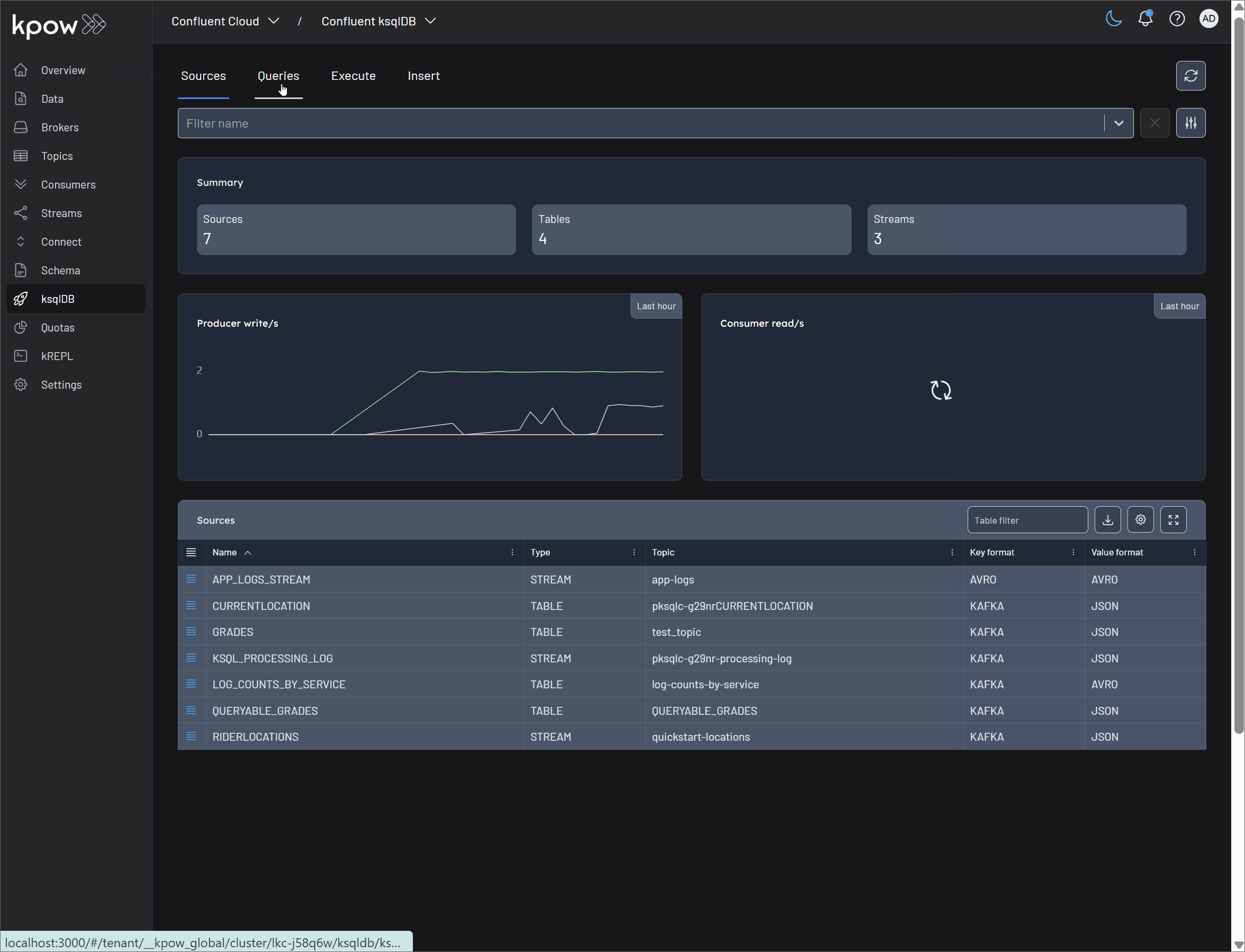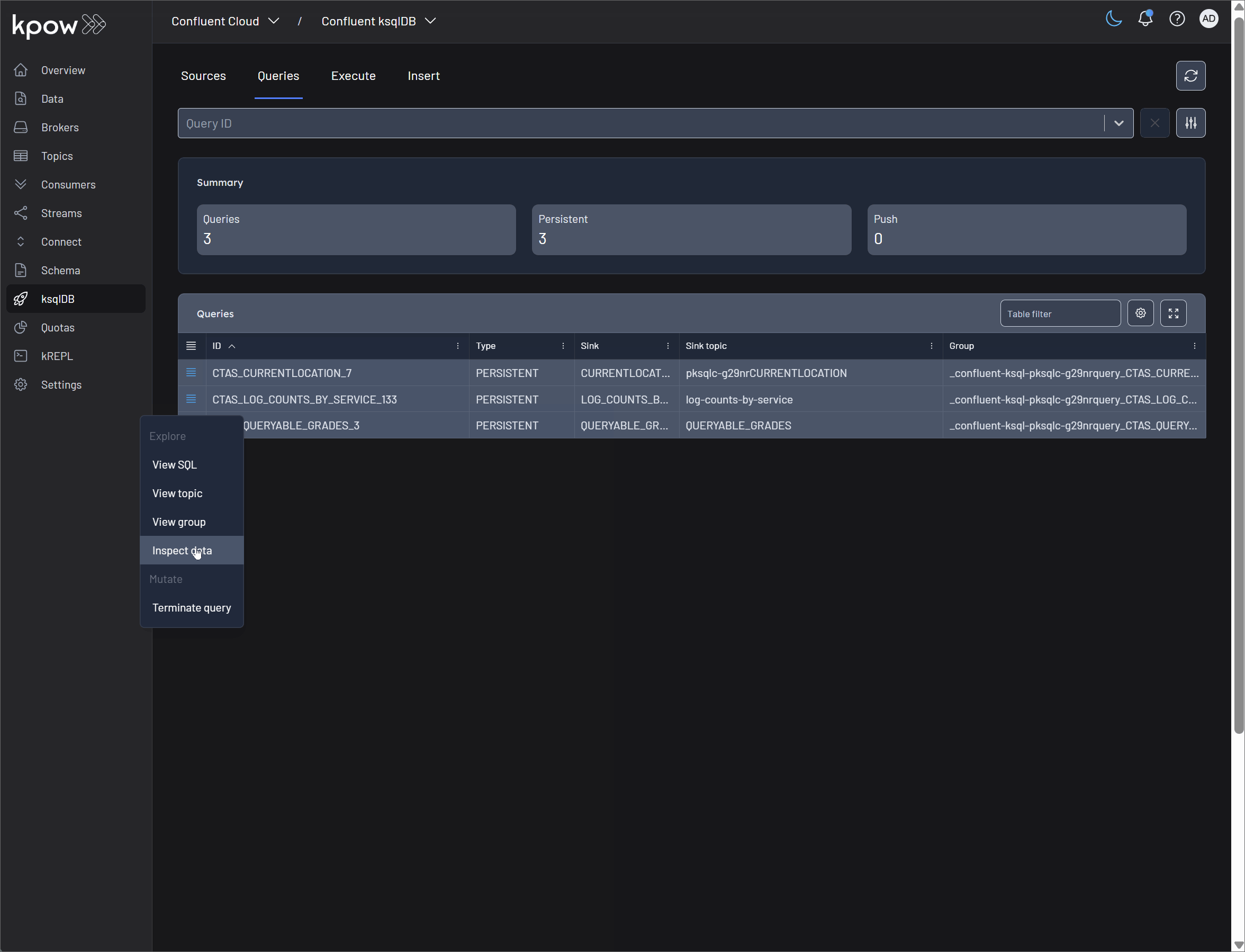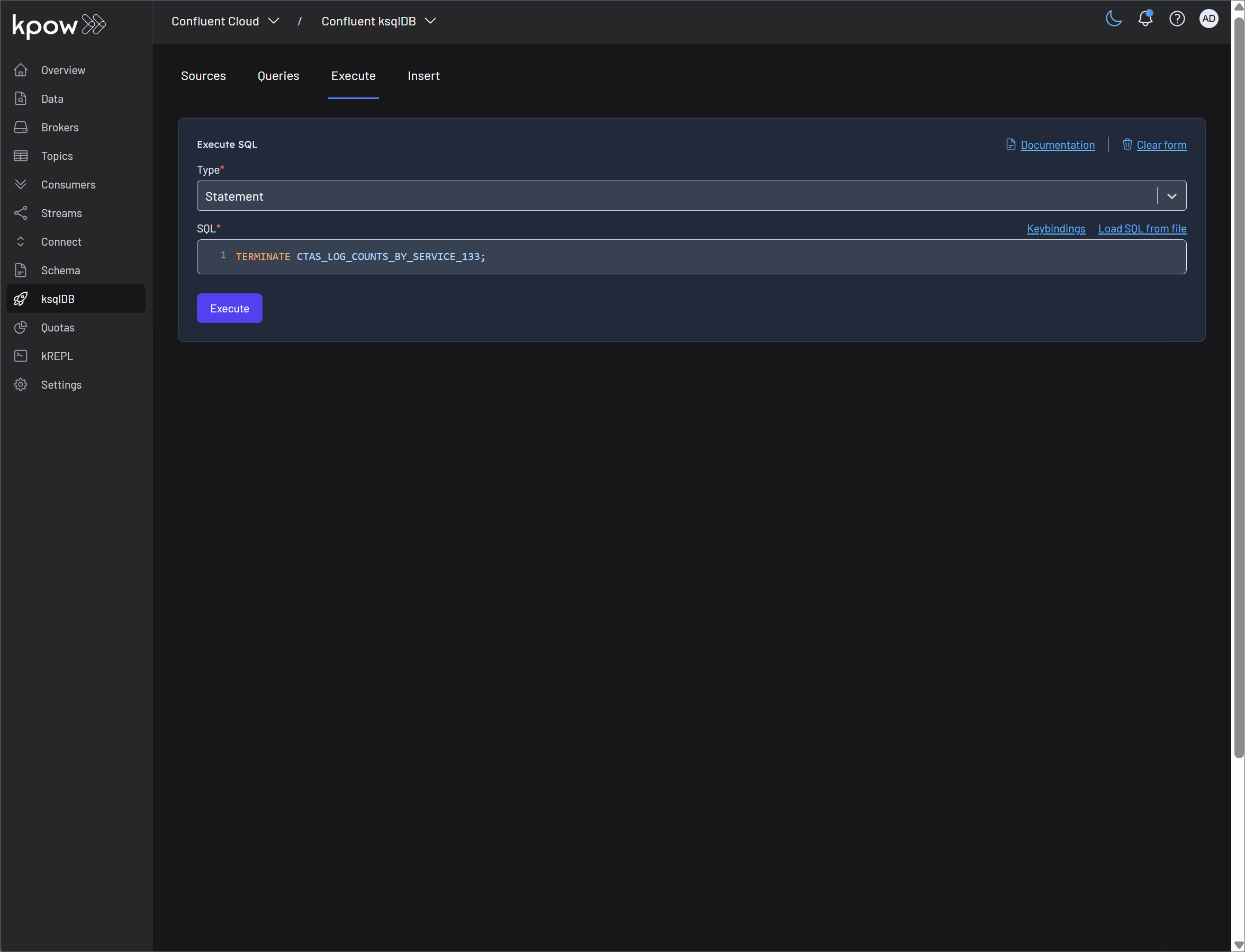
These features offer deep visibility into the state and behavior of a running ksqlDB query.
-
View SQL: This option displays the exact SQL statement that defines the persistent query. It's the ground truth for understanding what the query does, including its source streams or tables, filtering logic (
WHERE), transformations (SELECT), and aggregations (GROUP BY). -
View Topic: For any query that materializes its results (e.g.,
CREATE STREAM AS SELECT...orCREATE TABLE AS SELECT...), this provides a direct link to the sink Kafka topic. Clicking this takes you to Kpow's detailed topic view, where you can see the configuration and metrics for the topic receiving the query's output. -
View Group: Every persistent ksqlDB query is powered by a Kafka consumer group that reads from the source topics. This option links directly to that consumer group's dashboard in Kpow. It is critical for monitoring the health of the query, allowing you to check for consumer lag, which indicates if your query is falling behind in processing incoming data.
-
Inspect Data: This powerful feature allows you to see the real-time results being produced by your query. It uses Kpow's Data Inspect functionality on the query's sink topic, letting you view the actual messages as they are written. This is invaluable for debugging logic and verifying that the output is correct.
Mutate Option
This provides the ability to control the execution state of a query.
- Terminate Query: Persistent queries in ksqlDB run continuously until they are explicitly stopped. The Terminate query button in Kpow allows you to immediately halt the execution of a query. This is a crucial administrative function for stopping queries that are no longer needed, are behaving incorrectly, or need to be replaced by a newer version.
SQL execution
Kpow's SQL execution environment for ksqlDB is designed to be both powerful and secure, catering to both interactive exploration and production-level deployments.
-
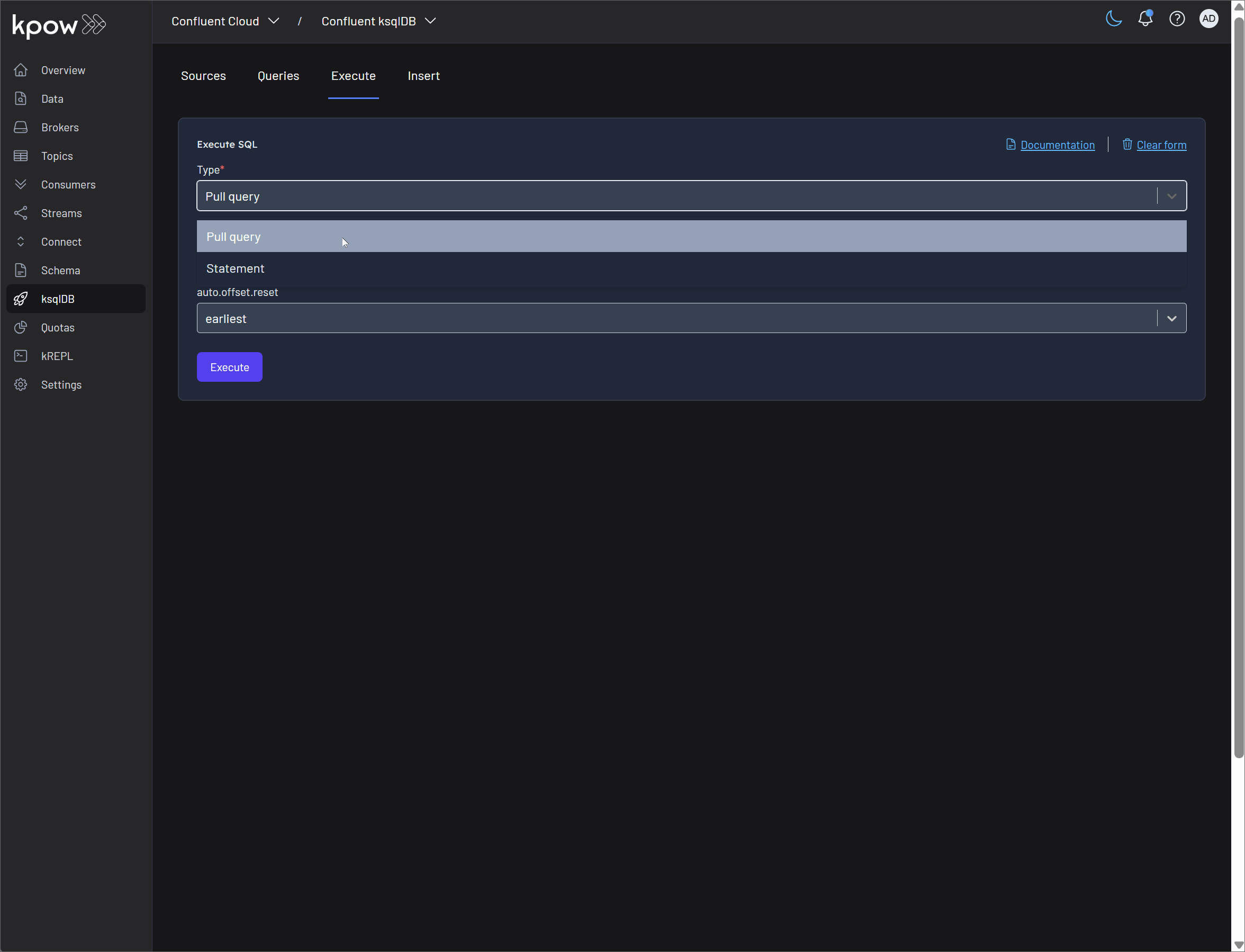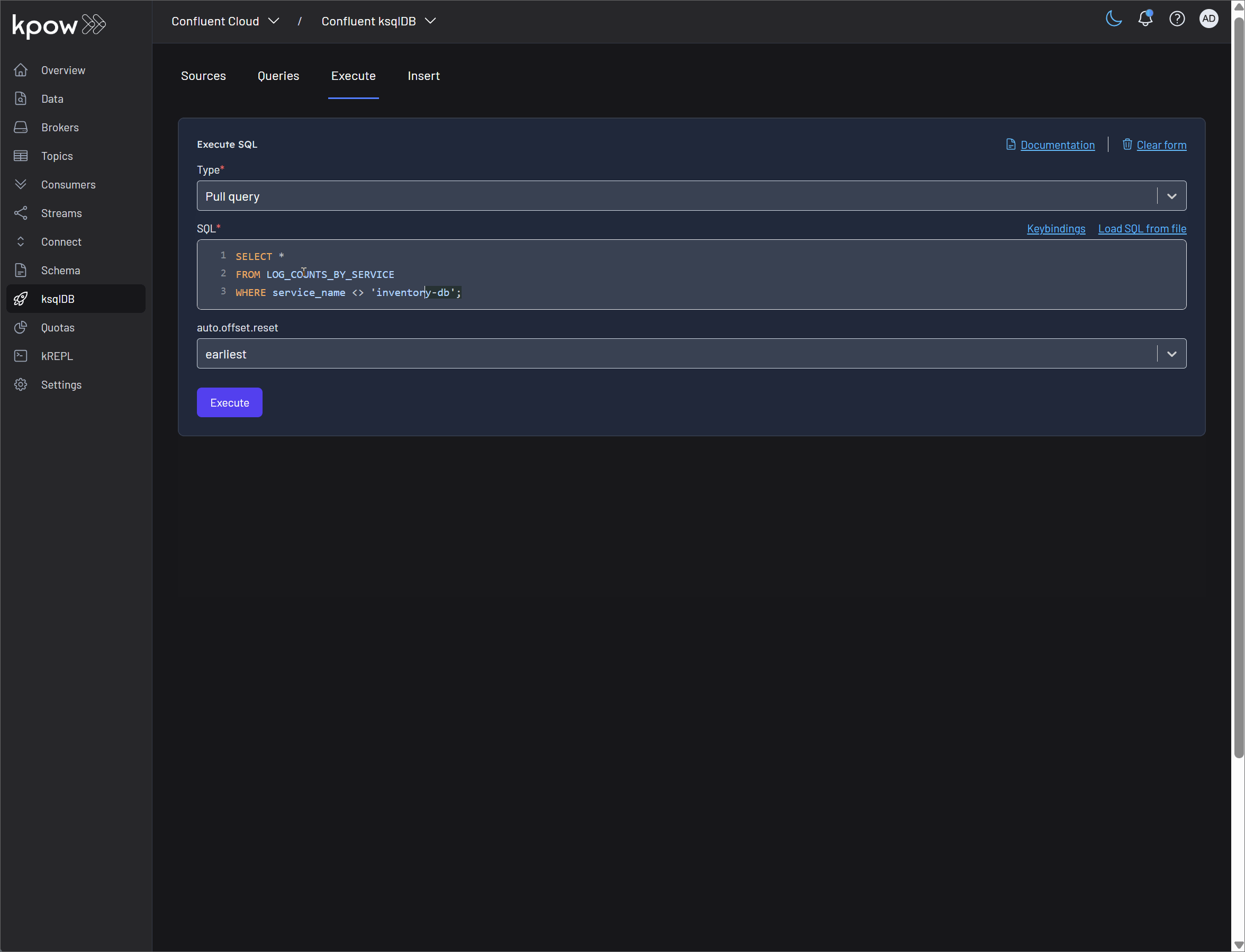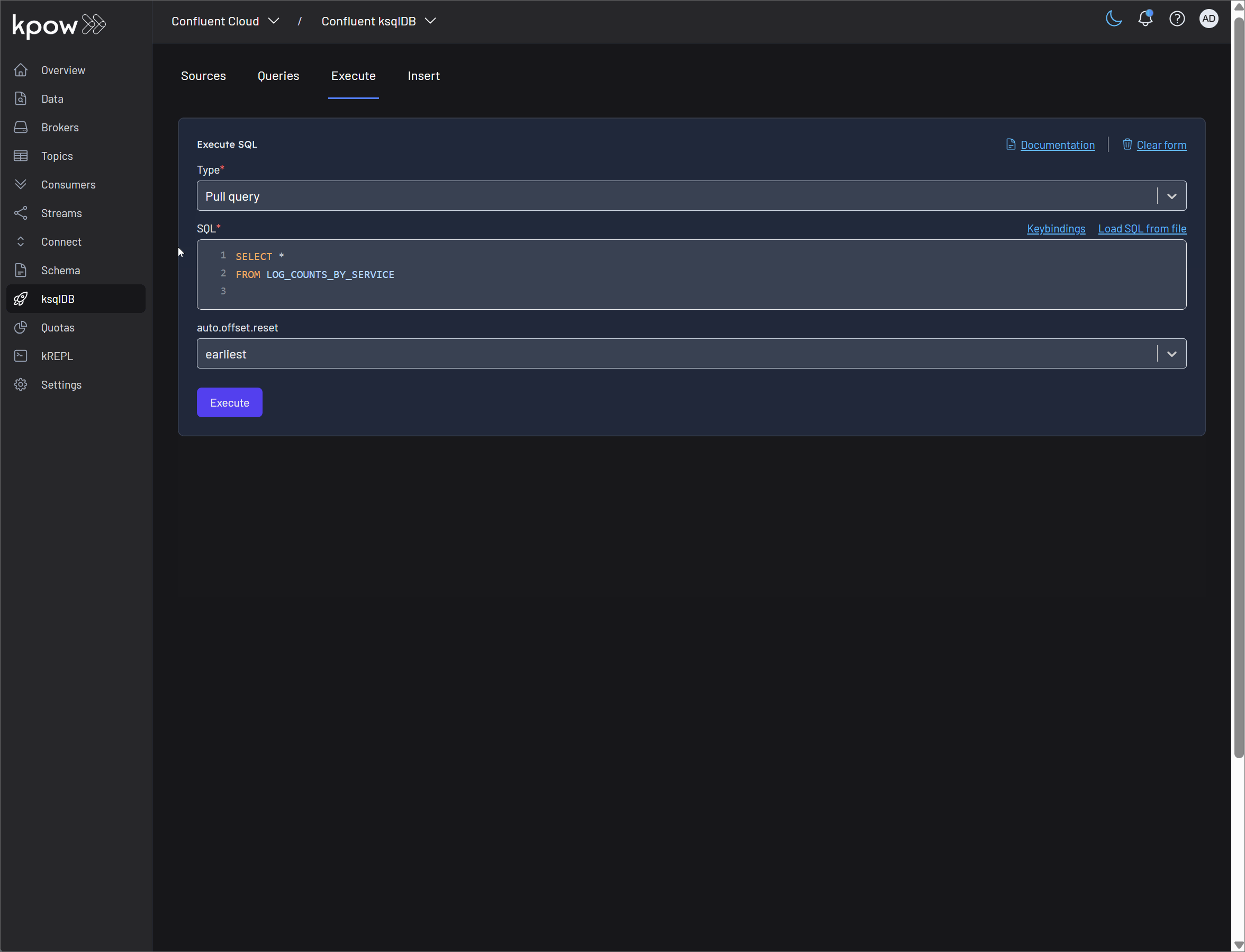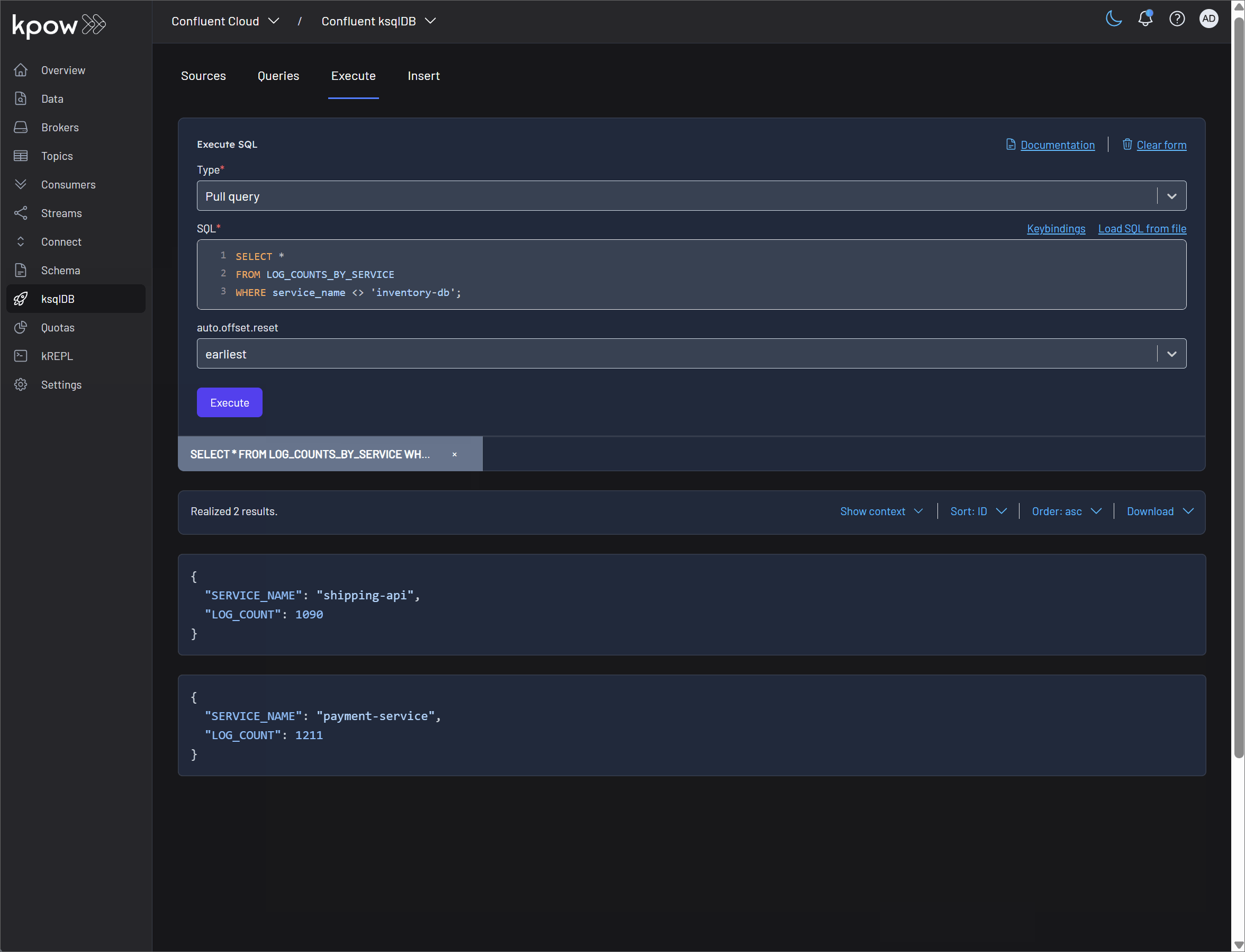
Pull query: Kpow fully supports the execution of pull queries, which retrieve the current state of a materialized view and then terminate. This is ideal for request-response interactions with your streaming data. The SQL editor in Kpow enhances this experience with:
- Intellisense/Autocomplete/REPL History: The embedded editor features intelligent code completion and a history of your previously executed queries, significantly speeding up development and exploration.
- Loading SQL from a File: For more complex or version-controlled queries, Kpow allows you to load SQL statements directly from a file. This feature, which may not be immediately obvious, is incredibly useful for deploying predefined queries and managing your SQL code base effectively.
- Integration with RBAC and Data Masking: All query executions are subject to Kpow's robust RBAC and data masking policies. This ensures that users can only access the data they are authorized to see, and sensitive information is redacted according to your defined policies.
-
Statement: Kpow's SQL console allows for the execution of all standard ksqlDB DDL and DML statements, including
CREATE TABLE,CREATE STREAM,DROP TABLE, andINSERT INTO. This provides a centralized and secure way to manage your ksqlDB schema and data.
Record insertion
Kpow simplifies the process of getting data into your ksqlDB sources with a flexible and user-friendly interface.
-
Insert Data: You can produce records directly into a ksqlDB stream or table in multiple ways:
- Manual Entry: Type or paste one or more records directly into the UI. This is ideal for quick tests, debugging, or inserting a small number of records.
- Import Rows from File: For bulk loading, Kpow allows you to import rows from a file. Supported formats include CSV (with headers), JSON, and EDN. This functionality is invaluable for populating tables and streams with initial or historical data.
-
View Schema: To ensure data is formatted correctly, the View schema button displays the expected Avro, Protobuf, or JSON schema for the records. This makes it simple to construct valid records and helps prevent data insertion errors.