Self-managed Kafka
Opting for a self-managed Apache Kafka setup gives us complete control over our Kafka environment. This approach allows for deep customization of our cluster's configuration and is ideal for specific use cases that a managed service might not support. While it requires us to handle the operational responsibilities of managing the cluster, it can be a cost-effective solution, especially for those who already have on-premises infrastructure.
Quickstart
We will start by launching a single-node Apache Kafka cluster, a Kafka Connect instance, and a Kpow instance using Docker Compose. This provides a complete local environment for developing and testing our Kafka applications.
The Schema Registry is not included in the open source Kafka distribution and is therefore not covered in this guide. However, Kpow provides robust support for Confluent-compatible schema registries. For more information on how Kpow integrates with Confluent Schema Registry, Apicurio Registry, and Karapace, see this post.
Here is a breakdown of the services defined in the docker-compose.yml file:
-
Kafka Broker (
broker)- Image:
apache/kafka:latest - Host Ports:
9092: Exposes the Kafka API to the host machine.
- Configuration:
- Mode: Runs a single node in KRaft mode, acting as both a broker and a controller.
- Listeners: Configured with multiple listeners. The
INTERNALlistener onbroker:19092is used for communication within the Docker network (e.g., from Connect and Kpow). TheEXTERNALlistener onlocalhost:9092is for applications running on the host machine.
- Image:
-
Kafka Connect (
connect)- Image:
apache/kafka:latest - Host Ports:
8083: Exposes the Kafka Connect REST API, accessible athttp://localhost:8083.
- Configuration:
- Bootstrap Servers: The
connect-distributed.propertiesfile configures thebootstrap.serversto connect to the Kafka broker atbroker:19092. - Dependencies: Explicitly depends on the
brokerservice to ensure Kafka is available before Connect starts. - Volumes: Mounts a local
connect-distributed.propertiesfile for configuration.
- Bootstrap Servers: The
- Image:
-
Kpow (
kpow)- Image:
factorhouse/kpow-ce:latest - Host Ports:
3000: Exposes the Kpow web UI, accessible athttp://localhost:3000.
- Configuration:
setup.env: All configuration is loaded from thesetup.envfile.BOOTSTRAP: Configured to connect to the broker atbroker:19092.CONNECT_REST_URL: Set tohttp://connect:8083to monitor and manage the Kafka Connect cluster.- Licensing: Requires your Kpow license details to be set in the
setup.envfile. - Dependencies: Explicitly depends on the
connectservice.
- Image:
docker-compose.yml
services:
broker:
image: apache/kafka:latest
container_name: broker
ports:
- "9092:9092"
environment:
KAFKA_NODE_ID: 1
KAFKA_PROCESS_ROLES: broker,controller
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES: CONTROLLER
KAFKA_LISTENERS: INTERNAL://broker:19092,CONTROLLER://broker:9094,EXTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9092
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: INTERNAL://broker:19092,EXTERNAL://localhost:9092
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: INTERNAL
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_QUORUM_VOTERS: 1@broker:9094
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: 1
KAFKA_GROUP_INITIAL_REBALANCE_DELAY_MS: 0
connect:
image: apache/kafka:latest
container_name: connect
command: >
/opt/kafka/bin/connect-distributed.sh
/opt/kafka/config/connect-distributed.properties
depends_on:
- broker
ports:
- "8083:8083"
volumes:
- ./connect-distributed.properties:/opt/kafka/config/connect-distributed.properties
kpow:
image: factorhouse/kpow-ce:latest
container_name: kpow-ce
pull_policy: always
restart: always
ports:
- "3000:3000"
depends_on:
- connect
env_file:
- setup.env
connect-distributed.properties
# Connect to the broker using its Docker network name and internal listener port
bootstrap.servers=broker:19092
# --- The rest of your configuration ---
rest.port=8083
rest.advertised.host.name=localhost
group.id=kafka-connect-cluster
key.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
config.storage.topic=__connect-configs
offset.storage.topic=__connect-offsets
status.storage.topic=__connect-status
config.storage.replication.factor=1
offset.storage.replication.factor=1
status.storage.replication.factor=1
# This path MUST exist for connectors to be found
plugin.path=/opt/kafka/plugins
setup.env
## Kafka environments
ENVIRONMENT_NAME=OSS Kafka
BOOTSTRAP=broker:19092
CONNECT_NAME=OSS Connect Cluster
CONNECT_REST_URL=http://connect:8083
## Your License Details
LICENSE_ID=<license-id>
LICENSE_CODE=<license-code>
LICENSEE=<licensee>
LICENSE_EXPIRY=<license-expiry>
LICENSE_SIGNATURE=<license-signature>
To launch the entire stack, we need to ensure the docker-compose.yml, connect-distributed.properties, and setup.env files are in the same directory. Then, we run the following command:
docker-compose up -d
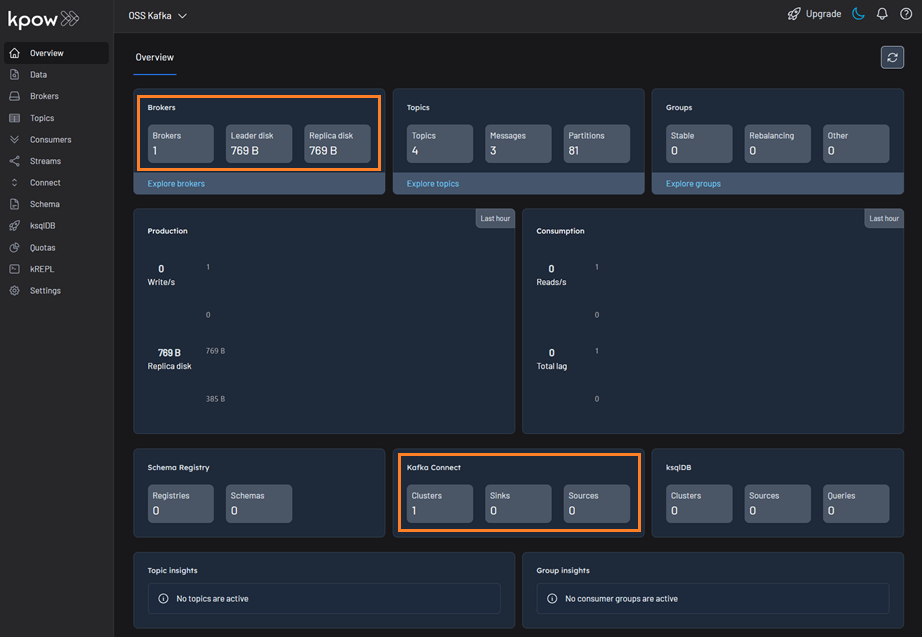
Once the containers are up and running, we can open our web browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000 to access the Kpow UI. We will find that Kpow has automatically detected and connected to our Kafka broker and Kafka Connect cluster.