Redpanda
What is Redpanda?
Redpanda offers a simple, powerful, and Kafka®-compatible streaming data platform. Kpow provides a rich, developer-focused UI to manage and monitor it. Together, they form a robust stack for building and operating real-time data pipelines.
Quickstart
Check out Integrate Kpow with the Redpanda Streaming Platform for more details and step-by-step instructions.
Let's begin by creating a dedicated Docker network named factorhouse, which establishes a private communication channel for the Redpanda and Kpow containers. Then launch a single Redpanda broker and Kpow instance in dedicated containers.
Here's an overview of the containers:
- Redpanda (
redpanda)- Image:
redpandadata/redpanda:latest - Host Ports:
19092: Exposes the Kafka API to the host machine.18081: Exposes the Schema Registry API to the host machine.
- Configuration:
- Mode: Runs in
dev-containermode, optimized for a single-node development environment. - Kafka API: Listens for connections internally on port
9092and externally on19092. It advertises itself asredpanda:9092within the Docker network andlocalhost:19092to the host. - Schema Registry: The built-in schema registry is enabled, listening internally on
8081and externally on18081.
- Mode: Runs in
- Network: Attached to the
factorhousenetwork, making it reachable by other containers at the hostnameredpanda.
- Image:
- Kpow (
kpow)- Image:
factorhouse/kpow-ce:latest(Usefactorhouse/kpow:latestfor the enterprise edition) - Host Port:
3000(for accessing the Kpow web UI from a browser athttp://localhost:3000). - Configuration:
- BOOTSTRAP: Configured to connect to the Redpanda cluster at
redpanda:9092, using the internal Docker network for communication. - SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: Configured to connect to Redpanda's integrated schema registry at
http://redpanda:8081. - SCHEMA_REGISTRY_OBSERVATION_VERSION: Set this to
1to ensure Kpow uses the observation mode compatible with Redpanda's Schema Registry. - ENVIRONMENT_NAME: Sets a descriptive name for the cluster that appears in the Kpow UI.
- Licensing: The configuration is loaded from an environment file specified by the
$KPOW_LICENSE_FILEshell variable, which is required to run the container.
- BOOTSTRAP: Configured to connect to the Redpanda cluster at
- Network: Attached to the
factorhousenetwork, allowing it to resolve and connect to theredpandacontainer.
- Image:
## Create a docker network to be shared
docker network create factorhouse
## Start a Redpanda cluster and schema registry
docker run -d -p 19092:19092 -p 18081:18081 --name redpanda --hostname redpanda --network factorhouse \
redpandadata/redpanda:latest redpanda start \
--kafka-addr internal://0.0.0.0:9092,external://0.0.0.0:19092 \
--advertise-kafka-addr internal://redpanda:9092,external://localhost:19092 \
--schema-registry-addr internal://0.0.0.0:8081,external://0.0.0.0:18081 \
--rpc-addr redpanda:33145 \
--advertise-rpc-addr redpanda:33145 \
--mode dev-container
## Start a Kpow instance
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name kpow --network factorhouse \
-e ENVIRONMENT_NAME="Local Redpanda Cluster" \
-e BOOTSTRAP="redpanda:9092" \
-e SCHEMA_REGISTRY_NAME="Local Repanda Registry" \
-e SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL="http://redpanda:8081" \
--env-file=$KPOW_LICENSE_FILE \
factorhouse/kpow-ce:latest
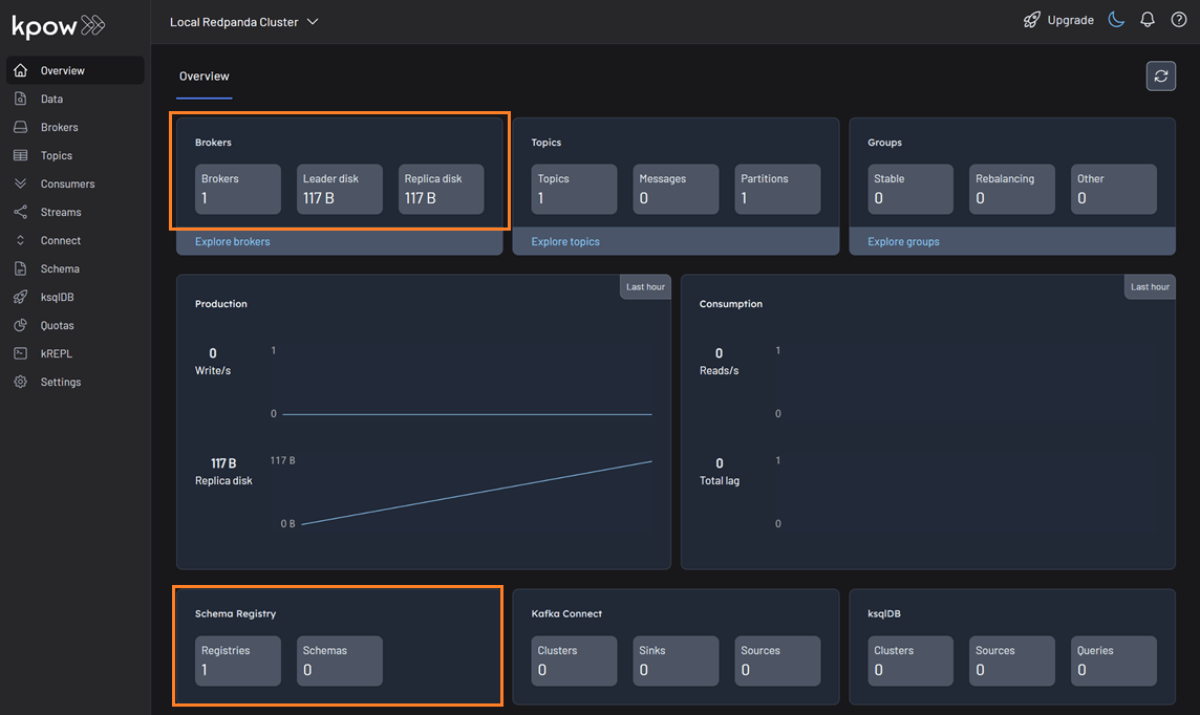
Once the containers are running, navigate to http://localhost:3000 to access the Kpow UI. We can see that Kpow has automatically discovered and connected to the single Redpanda broker and its schema registry.