Lab 2: Kafka Connect - Managing Kafka Source and Sink Connectors via Kpow UI and API
Explore how to deploy and manage Kafka Connect source and sink connectors using the Kpow UI and API. This lab walks through practical examples for configuring connectors that move data between Kafka and external systems.
How to start
Clone project repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/examples.git
cd examples
Start Kafka and Flink environments
We'll use Factor House Local to quickly spin up a Kafka environment that includes Kpow and MinIO. This setup uses the Kpow Enterprise edition, as we'll later rely on the Kpow API - an enterprise-only feature. Before you begin, ensure you have a valid Kpow license. For guidance on requesting and configuring a license, see this section of the project README.
## Clone the Factor House Local Repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/factorhouse-local.git
## Download Kafka/Flink Connectors and Spark Iceberg Dependencies
./factorhouse-local/resources/setup-env.sh
## Uncomment the sections to enable the edition and license.
# Edition (choose one):
# unset KPOW_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# unset FLEX_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# export KPOW_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# export FLEX_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# Licenses:
# export KPOW_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
# export FLEX_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml up -d \
&& docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml up -d
Deploy source connector via UI
We will use the MSK Data Generator (source) and Confluent S3 (sink) connectors. Let's first create the source connector using the Kpow UI.
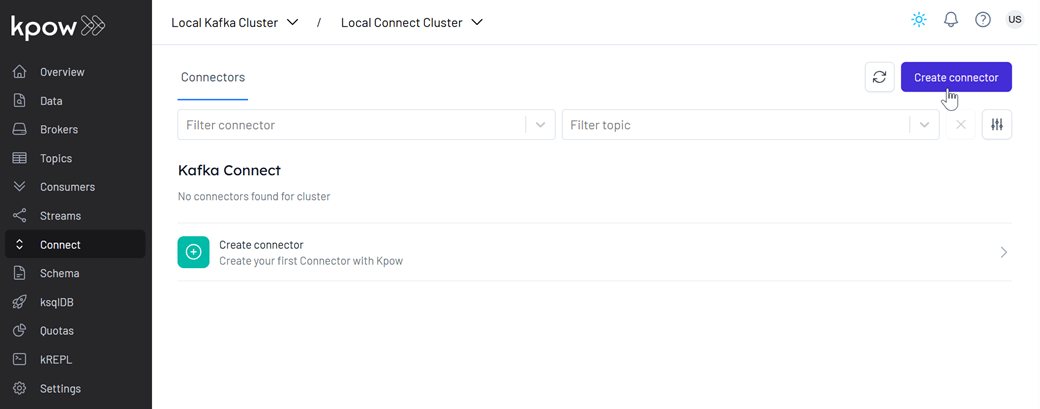
- Open the Kpow UI at
http://localhost:3000and log in using the credentialsadmin/admin. Then, navigate to the Connect section. - Click Create connector to get started.
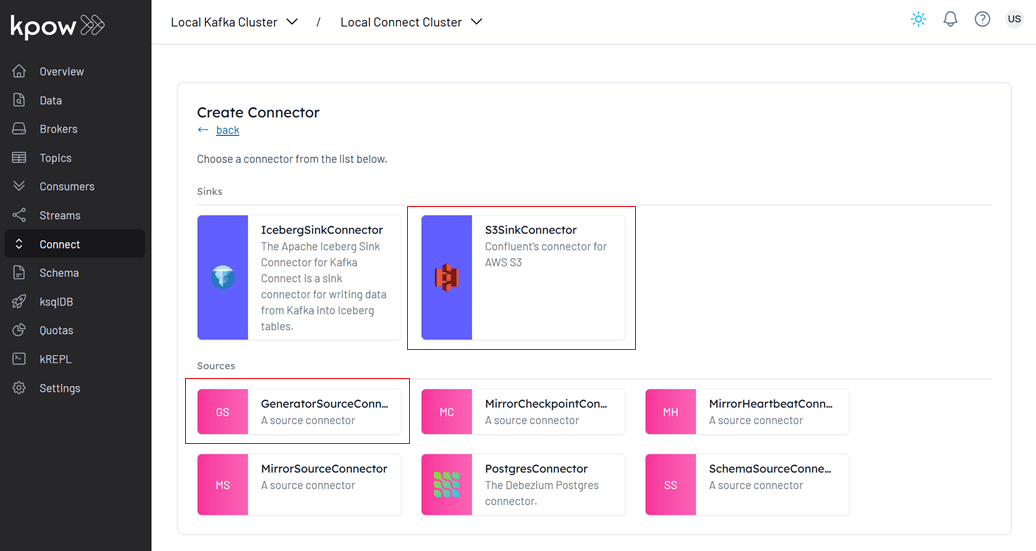
- Select the GeneratorSourceConnector connector
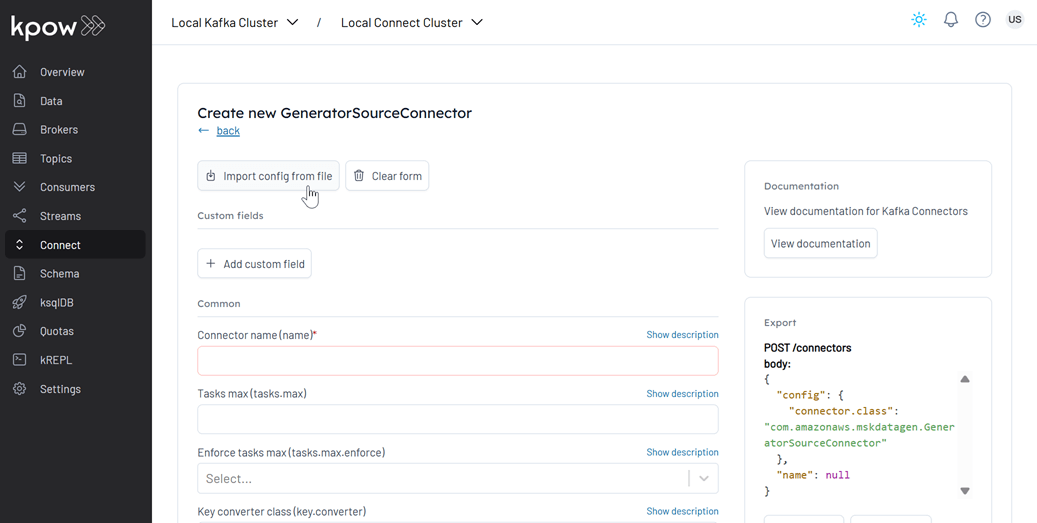
- Import the source connector configuration file (
./fh-local-labs/lab-02/orders-source.json) and hit Create.
- Once deployed, we can check the source connector and its tasks in the Kpow UI.
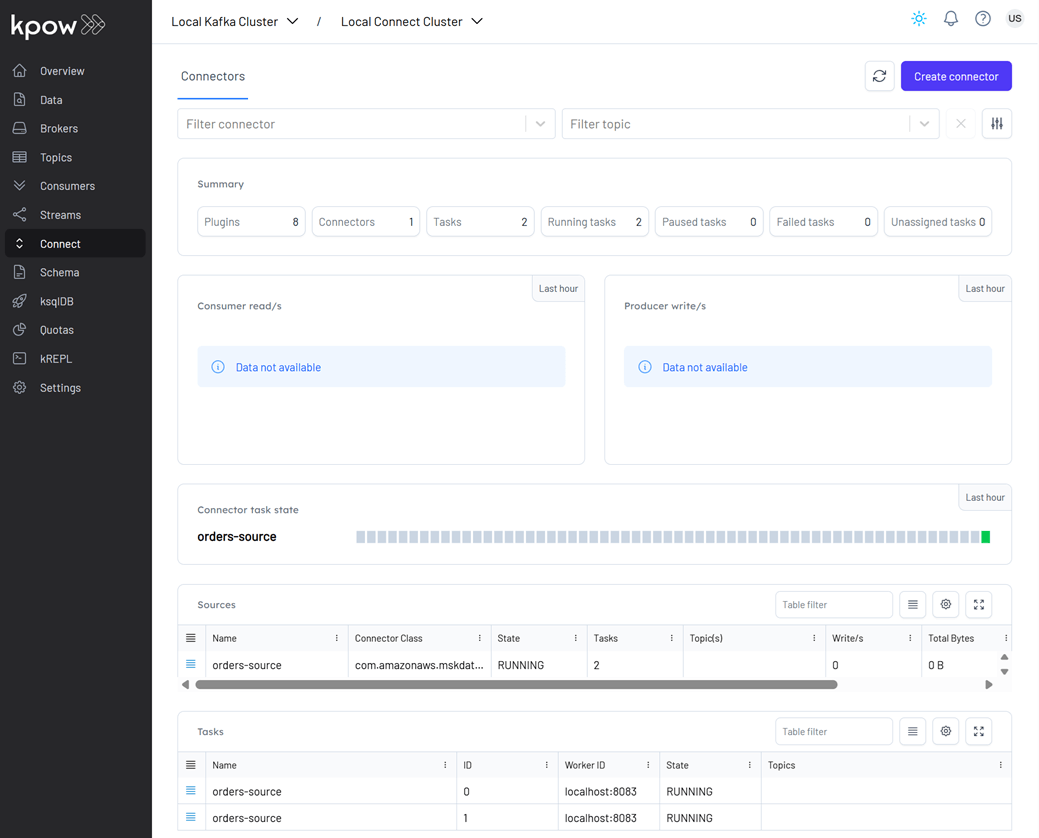
The value schema for the orders topic (orders-value) is registered as a record type. However, by default, the source connector generates a union schema (e.g., ["null", "record"]) to allow for nullable records. The S3 Sink Connector, on the other hand, expects a value schema of type record, not a union. To resolve this mismatch, a custom Single Message Transform (SMT) — io.factorhouse.smt.UnwrapUnionTransform - is used to unwrap the union and expose only the record type. Note: Do not configure tombstone records when using this transform, as null values are incompatible with the unwrapped record schema.
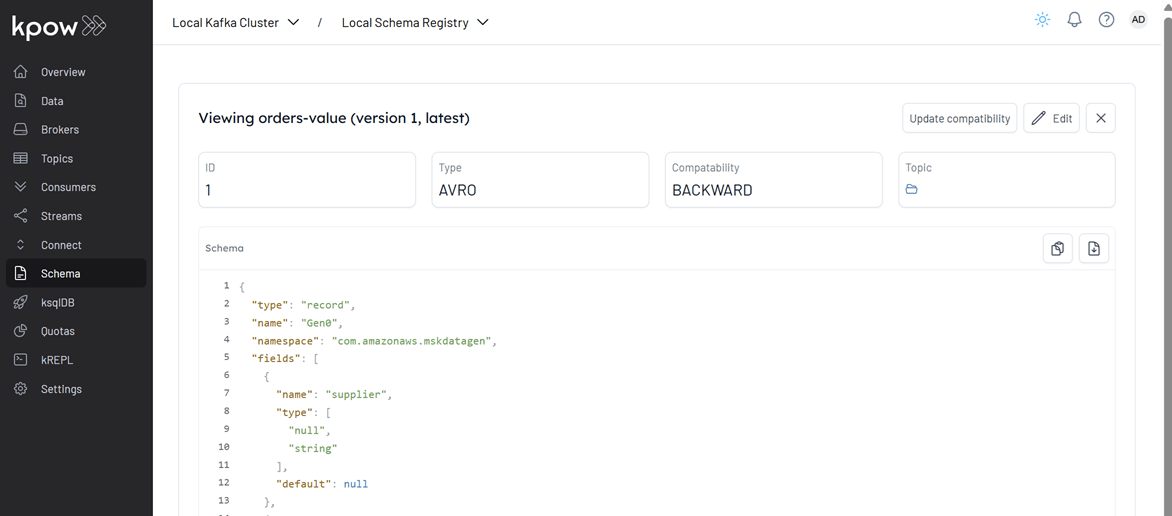
This connector will start producing mock order data to a Kafka topic (orders).
Deploy sink connector via API
Next, we'll create the Confluent S3 sink connector using the Kpow API.
- Generate base64 encoded value of an API key.
Factor House Local pre-configures several users. For this demo, we'll use the admin:admin credentials. Note that the user has the kafka-users role, which includes the CONNECT_CREATE and CONNECT_DELETE permissions.
AUTH_HEADER=$(echo "Authorization: Basic $(echo -n 'admin:admin' | base64)")
- Get Kafka Connect cluster ID
To manage connectors via the API, we first need the Connect cluster ID. We'll store it in a separate variable.
curl -s -H "$AUTH_HEADER" http://localhost:4000/connect/v1/clusters
# {
# "clusters": [
# {
# "id": "<connect-cluster-id>",
# "label": "Local Connect Cluster",
# "type": "apache_connect"
# }
# ],
# "metadata": {
# "tenant_id": "__kpow_global"
# }
# }
CONNECT_ID=<connect-cluster-id>
This CONNECT_ID will be used in subsequent API calls to manage connectors.
- Create the Sink Connector
Now, make a POST request with the S3 sink connector configuration (fh-local-labs/lab-02/orders-sink.json).
curl -s -i -X POST -H "$AUTH_HEADER" -H "Accept:application/json" -H "Content-Type:application/json" \
http://localhost:4000/connect/v1/apache/$CONNECT_ID/connectors \
-d @fh-local-labs/lab-02/orders-sink.json
# {
# "name": "orders-sink",
# "metadata": {
# "response_id": "96a93504-6bd9-4ccc-bfbb-fd62d71ec88a",
# "cluster_id": "<cluster-id>",
# "is_staged": false,
# "connect_id": "<connect-cluster-id>",
# "tenant_id": "__kpow_global"
# }
# }
We can check the status of the API as shown below.
curl -s -H "$AUTH_HEADER" http://localhost:4000/connect/v1/apache/$CONNECT_ID/connectors/orders-sink
# {
# "name": "orders-sink",
# "type": "sink",
# "state": "RUNNING",
# "worker_id": "localhost:8083",
# "class": "io.confluent.connect.s3.S3SinkConnector",
# "topics": [],
# "tasks": [
# {
# "id": 0,
# "state": "RUNNING",
# "worker_id": "localhost:8083"
# },
# {
# "id": 1,
# "state": "RUNNING",
# "worker_id": "localhost:8083"
# }
# ],
# "metadata": {
# "connect_id": "<connect-cluster-id>",
# "tenant_id": "__kpow_global"
# }
# }
Verify data flow
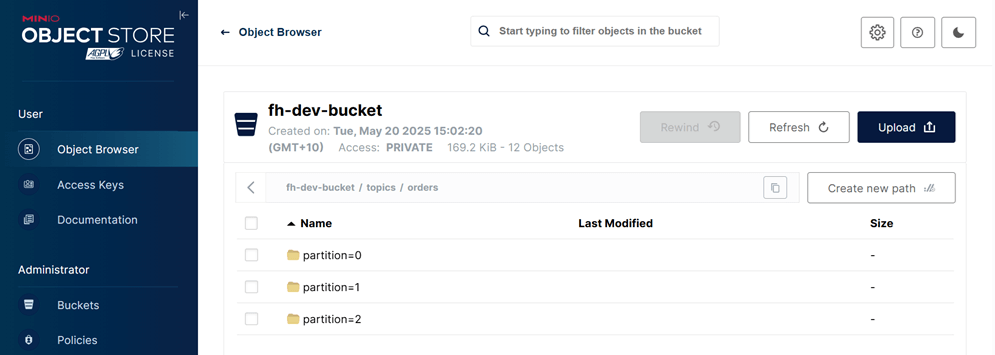
- Check Topic Data
Once the source connector is running, it begins producing messages. The sink connector, when started, consumes messages from the orders topic and writes them to the MinIO bucket (fh-dev-bucket), viewable at http://localhost:9001/. Records are stored in the path: topics/orders/partition=<num> within the bucket.
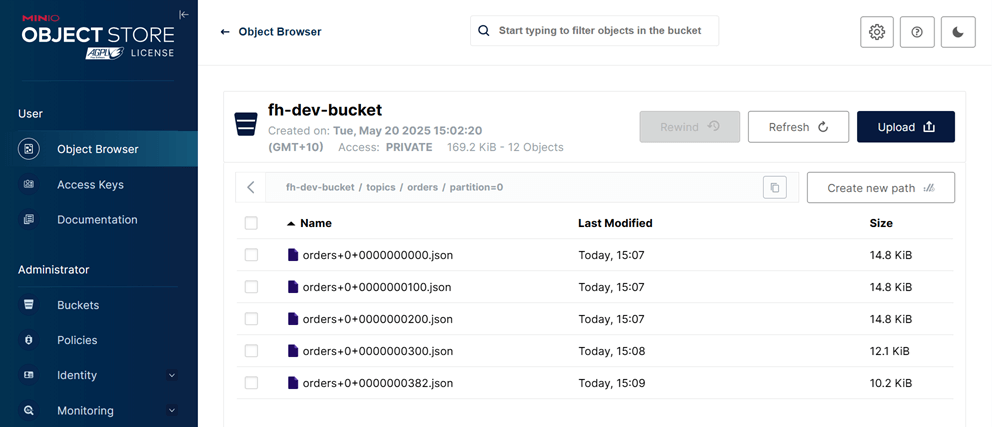
- Inspect Records
Each file contains at most 100 records in JSON Lines format, which you can verify by inspecting the contents.
Delete connectors
Now, let's clean up by deleting the connectors.
- Delete the sink connector via API
curl -X DELETE -H "$AUTH_HEADER" \
http://localhost:4000/connect/v1/apache/$CONNECT_ID/connectors/orders-sink
# {
# "metadata": {
# "response_id": "55b12842-e9eb-4e51-993b-053c62726e81",
# "cluster_id": "<cluster-id>",
# "is_staged": false,
# "connect_id": "<connect-cluster-id>",
# "tenant_id": "__kpow_global"
# }
# }
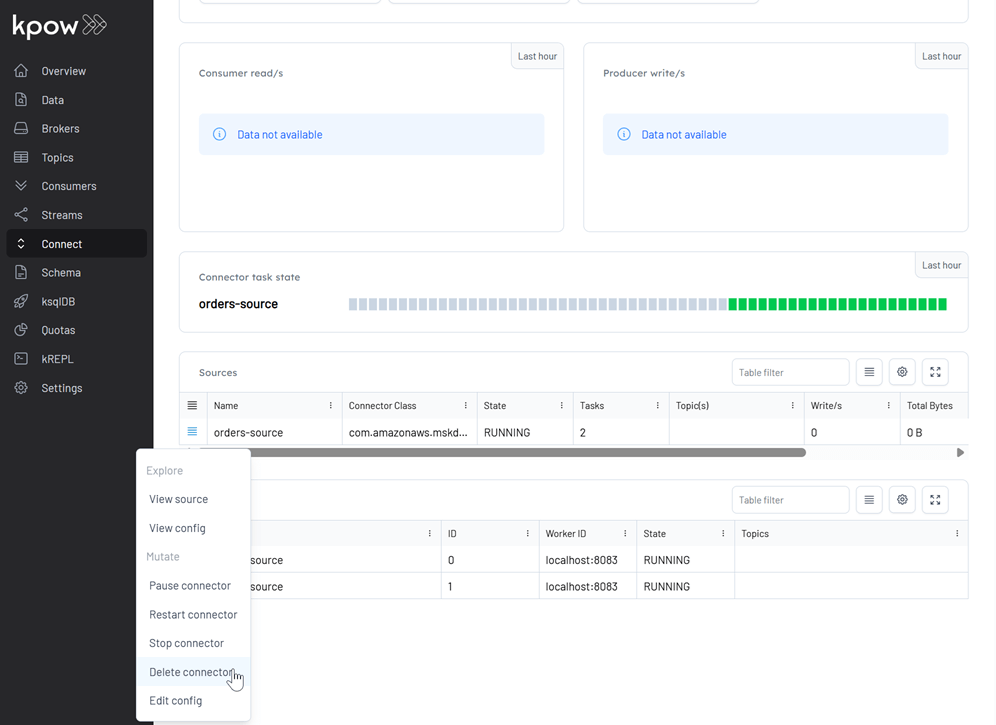
- Delete the source connector via UI:
Navigate to the Connect section, and click Delete connector option.
Shutdown environment
Finally, stop and remove the Docker containers.
If you're not already in the project root directory, navigate there first. Then, stop and remove the Docker containers by running:
# Stops the containers and unsets environment variables
docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml down \
&& docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml down
unset KPOW_SUFFIX FLEX_SUFFIX KPOW_LICENSE FLEX_LICENSE