Lab 9: Kafka Connect - Streaming Order Data from Kafka into Iceberg
Use Kafka Connect to stream Avro records from Kafka into an Iceberg table in MinIO. The lab covers connector deployment via Kpow and how to configure hidden partitioning using a Spark-defined table schema.
How to start
Clone project repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/examples.git
cd examples
Start Kafka and Flink environments
We'll use Factor House Local to quickly spin up a Kafka environments that includes Kpow as well as an analytics environment for Iceberg. We can use either the Community or Enterprise editions of Kpow. To begin, ensure valid licenses are available. For details on how to request and configure a license, refer to this section of the project README.
## Clone the Factor House Local Repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/factorhouse-local.git
## Download Kafka/Flink Connectors and Spark Iceberg Dependencies
./factorhouse-local/resources/setup-env.sh
## Uncomment the sections to enable the edition and license.
# Edition (choose one):
# unset KPOW_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# unset FLEX_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# export KPOW_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# export FLEX_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# Licenses:
# export KPOW_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
# export FLEX_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml up -d \
&& docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml up -d
Persistent Catalogs
Two catalogs are pre-configured in both the Flink and Spark clusters:
demo_hv: a Hive catalog backed by the Hive Metastoredemo_ib: an Iceberg catalog also backed by the Hive Metastore
Flink
In Flink, the catalogs can be initialized automatically using an SQL script (init-catalogs.sql) on startup:
CREATE CATALOG demo_hv WITH (
'type' = 'hive',
'hive-conf-dir' = '/opt/flink/conf',
'default-database' = 'default'
);
CREATE CATALOG demo_ib WITH (
'type' = 'iceberg',
'catalog-type' = 'hive',
'uri' = 'thrift://hive-metastore:9083'
);
Spark
In Spark, catalog settings are defined in spark-defaults.conf:
# Enable Iceberg extensions
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions
# Hive catalog (demo_hv)
spark.sql.catalog.demo_hv org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog
spark.sql.catalog.demo_hv.type hive
spark.sql.catalog.demo_hv.hive.metastore.uris thrift://hive-metastore:9083
spark.sql.catalog.demo_hv.warehouse s3a://warehouse/
# Iceberg catalog (demo_ib)
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.type hive
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.uri thrift://hive-metastore:9083
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.io-impl org.apache.iceberg.aws.s3.S3FileIO
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.s3.endpoint http://minio:9000
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.s3.path-style-access true
spark.sql.catalog.demo_ib.warehouse s3a://warehouse/
# Optional: set default catalog
spark.sql.defaultCatalog spark_catalog
Deploy source connector
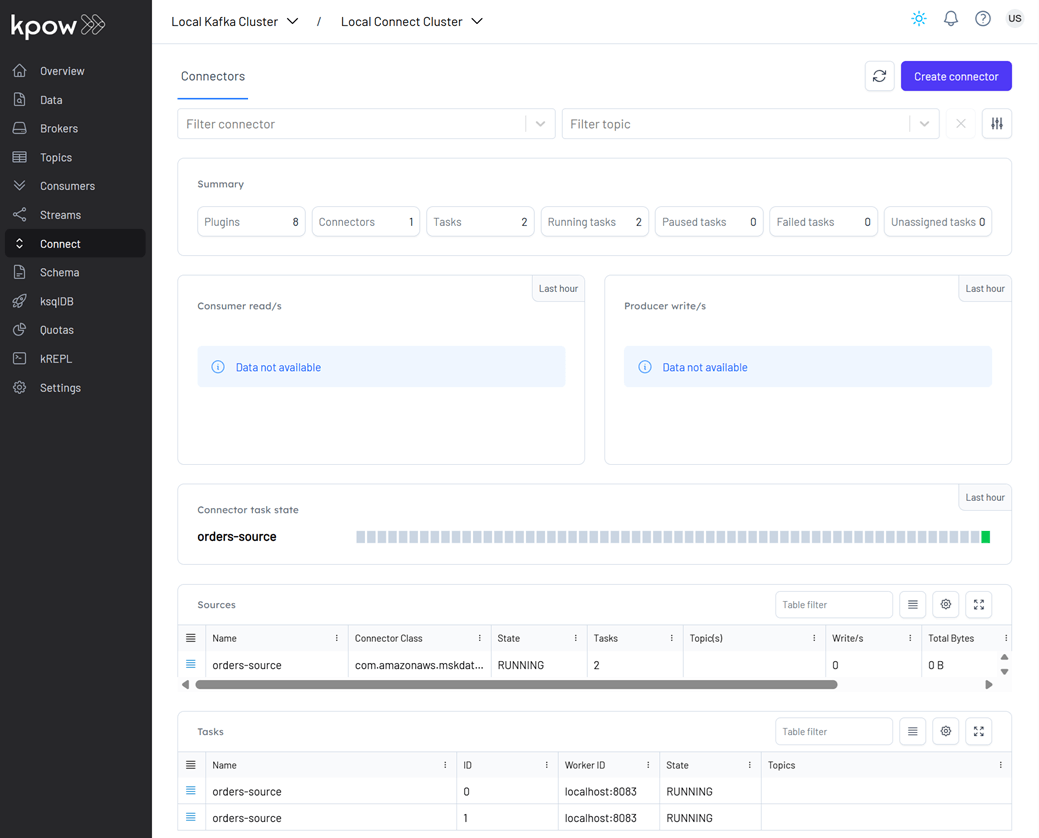
We will create a source connector that generates fake order records to a Kafka topic (orders). See the Kafka Connect via Kpow UI and API lab for details about how to create the connector.
Once deployed, we can check the connector and its tasks in Kpow.
Create sink table
The Iceberg sink connector requires that the target table already exists. We'll use Spark SQL to create the sink table.
docker exec -it spark-iceberg /opt/spark/bin/spark-sql
-- // Only 'spark_catalog' appears although 'demo_hv' and 'demo_ib' exists
SHOW CATALOGS;
-- spark_catalog
-- // If 'demo_ib' gets showing if being used.
USE demo_ib;
SHOW CATALOGS;
-- demo_ib
-- spark_catalog
-- // Use the `default` database
USE `default`;
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id STRING,
item STRING,
price DECIMAL(10, 2),
supplier STRING,
bid_time TIMESTAMP
)
USING iceberg
PARTITIONED BY (DAY(bid_time))
TBLPROPERTIES (
'format-version' = '2',
'write.format.default' = 'parquet',
'write.target-file-size-bytes' = '134217728',
'write.parquet.compression-codec' = 'snappy',
'write.metadata.delete-after-commit.enabled' = 'true',
'write.metadata.previous-versions-max' = '3',
'write.delete.mode' = 'copy-on-write',
'write.update.mode' = 'copy-on-write'
);
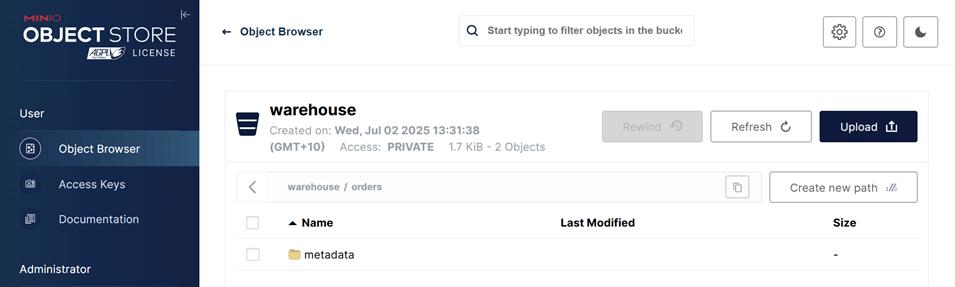
After creation, the table will initially contain only metadata (no data). We can view it in the MinIO Console at http://localhost:9001.
- Username:
admin - Password:
password
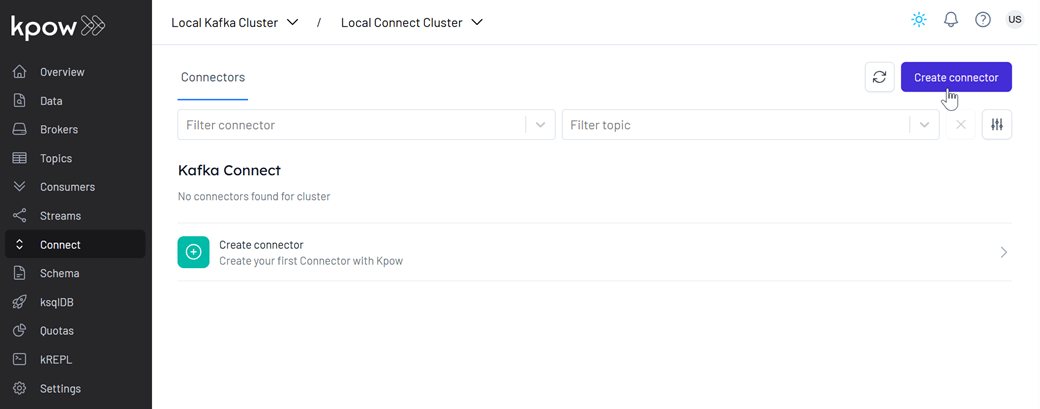
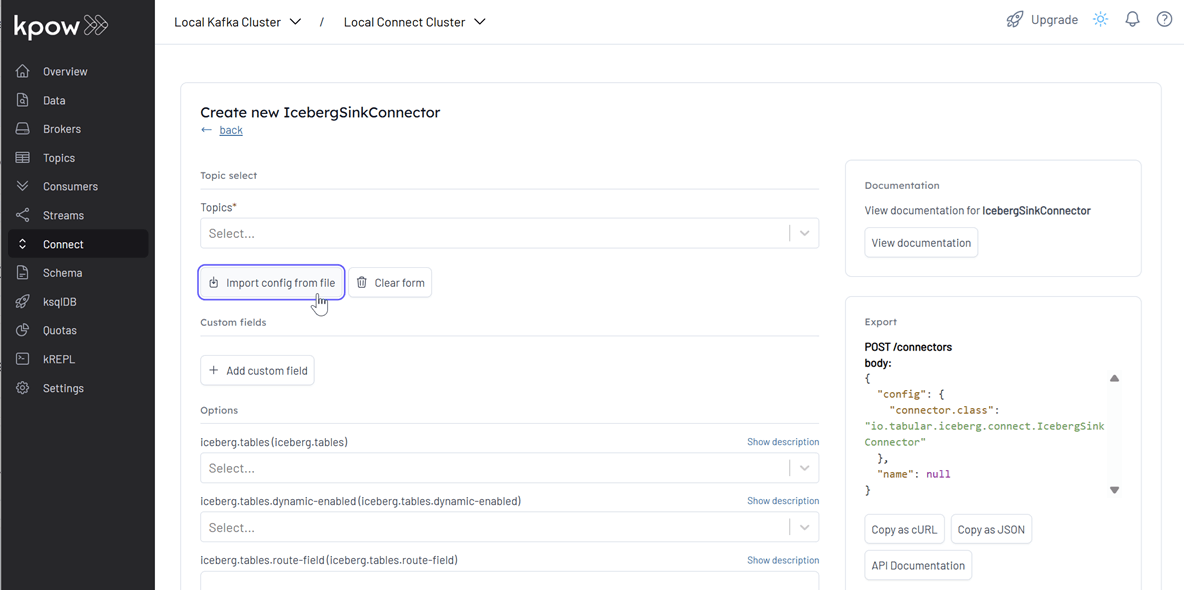
Create sink connector
- Open to the Kpow UI (http://localhost:3030) and go to the Connect section.
- Click Create connector to get started.
- Select the IcebergSinkConnector connector
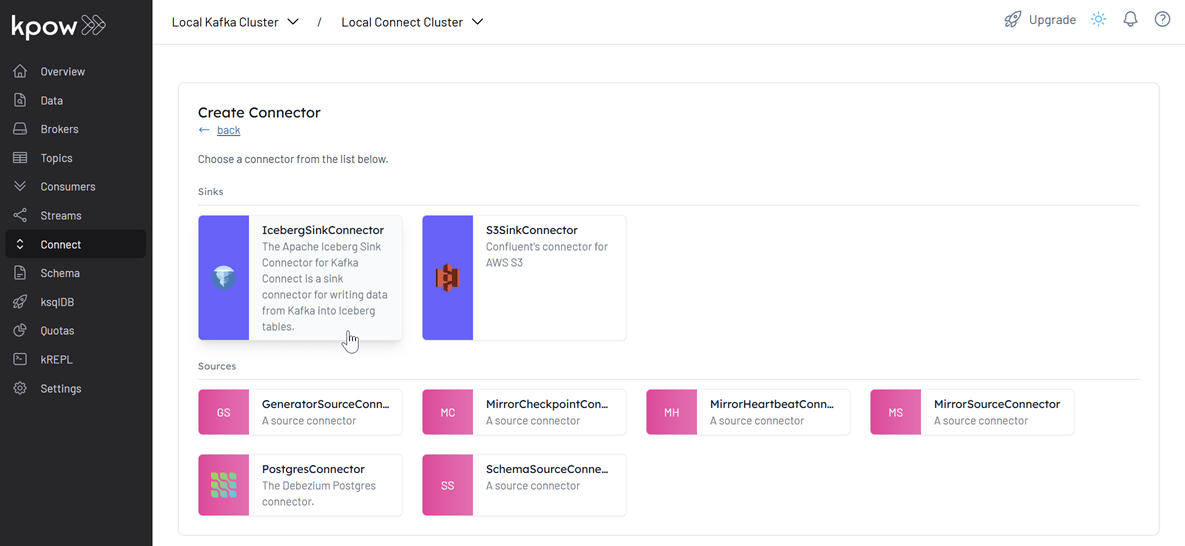
- Import the source connector configuration file (
./fh-local-labs/lab-09/orders-iceberg-sink.json) and hit Create.
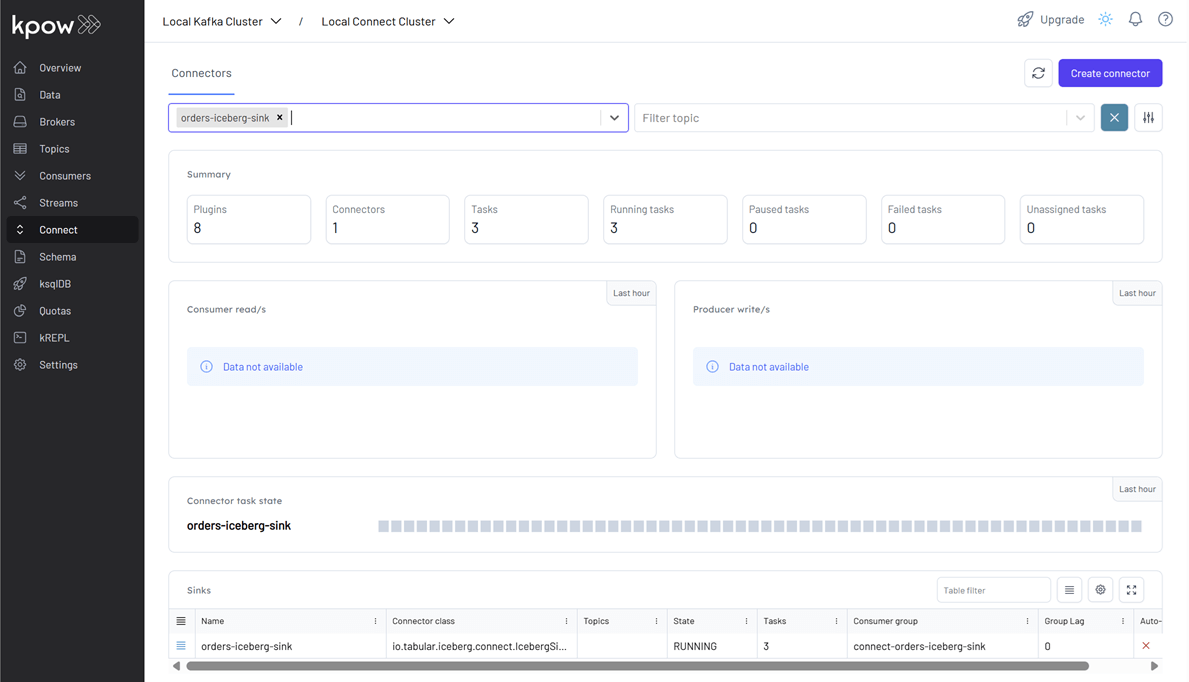
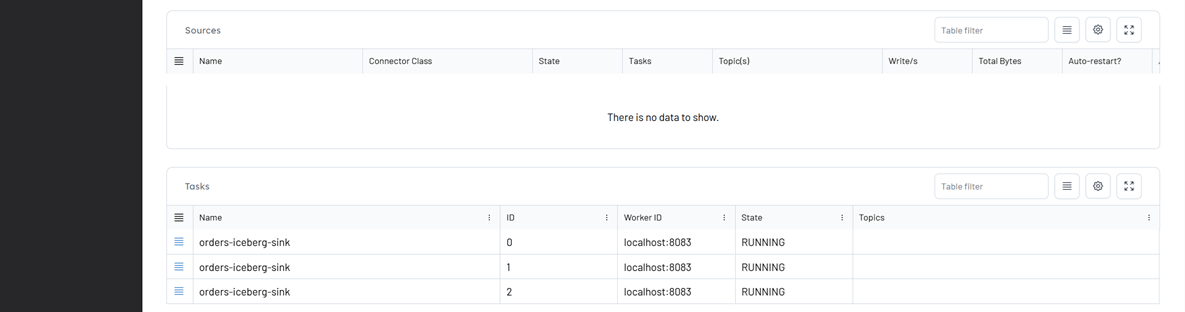
- After creation, we can monitor the connector and its tasks directly in Kpow.
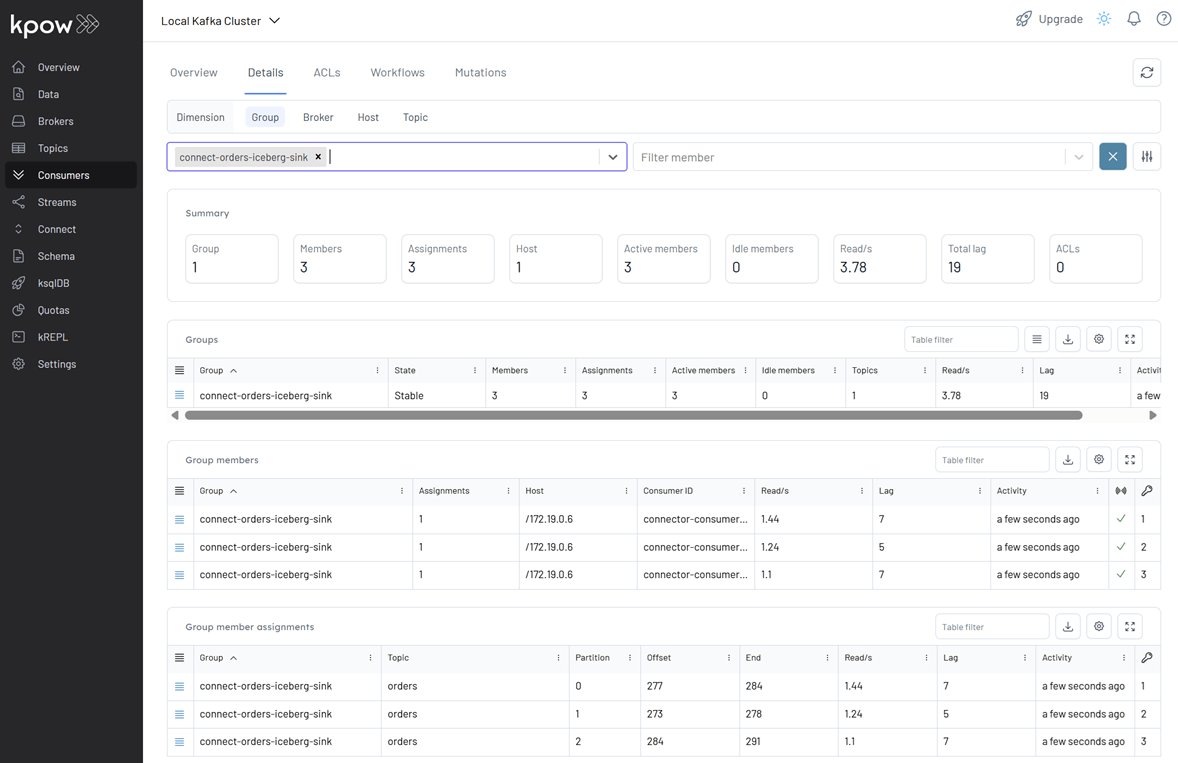
We can also track connector performance by filtering its consumer group (connect-orders-iceberg-sink) in the Consumers section. This displays key metrics like group state, assigned members, read throughput, and lag:
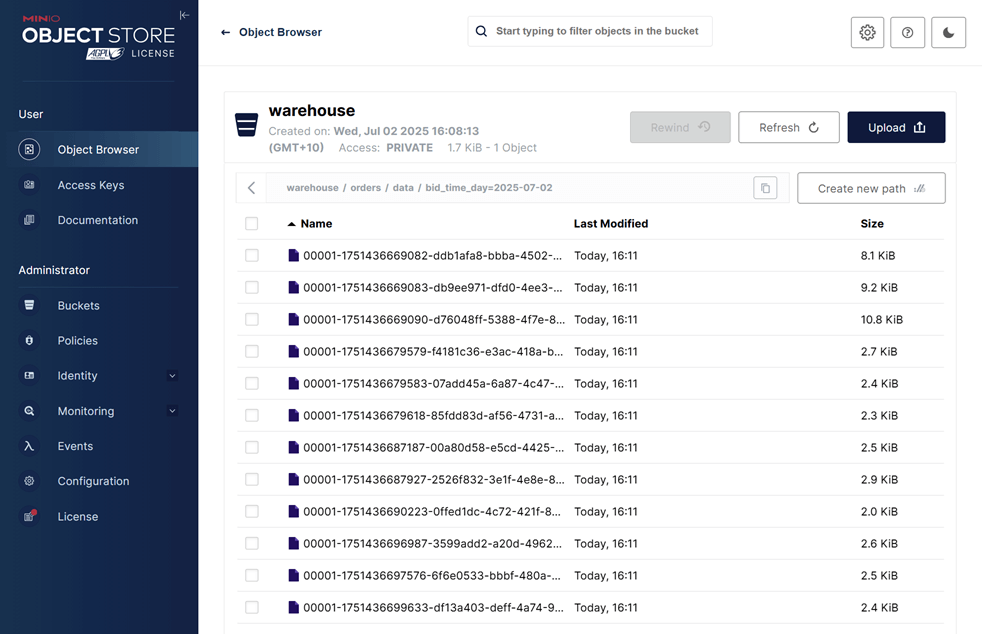
Finally, inspect the Parquet files written by the connector via MinIO at http://localhost:9001 using admin as the username and password as the password. As shown below, records are correctly partitioned and stored in the configured MinIO bucket (warehouse).
Shutdown environment
Finally, stop and remove the Docker containers.
If you're not already in the project root directory, navigate there first. Then, stop and remove the Docker containers by running:
# Stops the containers and unsets environment variables
docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml down \
&& docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml down
unset KPOW_SUFFIX FLEX_SUFFIX KPOW_LICENSE FLEX_LICENSE