Lab 11: Flink SQL Gateway - Serving Real-Time Supplier Stats via REST API
Run a Flink SQL streaming pipeline via the Flink SQL Gateway and access real-time query results through its REST API. This lab illustrates how to fetch and display live supplier statistics from a Kafka source using a Python client.
How to start
Clone project repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/examples.git
cd examples
Start Kafka and Flink environments
We'll use Factor House Local to quickly spin up Kafka and Flink environments that include Kpow and Flex. We can use either the Community or Enterprise editions of Kpow/Flex. To begin, ensure valid licenses are available. For details on how to request and configure a license, refer to this section of the project README.
Update Flink Custom Jar Loading
The Flink cluster loads custom dependency JAR files from the directories specified by the CUSTOM_JARS_DIRS environment variable in the compose-flex.yml file. Since the Flink SQL Gateway does not support dynamic JAR loading, the required JARs (e.g., Kafka and Avro) must be preloaded by setting the appropriate paths in the CUSTOM_JARS_DIRS variable.
Before:
x-common-environment: &flink_common_env_vars
AWS_REGION: us-east-1
HADOOP_CONF_DIR: /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop
CUSTOM_JARS_DIRS: "/tmp/hadoop;/tmp/hive;/tmp/iceberg;/tmp/parquet"
After:
x-common-environment: &flink_common_env_vars
AWS_REGION: us-east-1
HADOOP_CONF_DIR: /opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop
CUSTOM_JARS_DIRS: "/tmp/hadoop;/tmp/hive;/tmp/iceberg;/tmp/parquet;/tmp/connector"
This ensures the following JARs are loaded additionally into the Flink JobManager, TaskManagers, and SQL Gateway:
/tmp/connector/flink-sql-connector-kafka-3.3.0-1.20.jar/tmp/connector/flink-sql-avro-confluent-registry-1.20.1.jar
Start services:
## Clone the Factor House Local Repository
git clone https://github.com/factorhouse/factorhouse-local.git
## Download Kafka/Flink Connectors and Spark Iceberg Dependencies
./factorhouse-local/resources/setup-env.sh
## Uncomment the sections to enable the edition and license.
# Edition (choose one):
# unset KPOW_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# unset FLEX_SUFFIX # Enterprise
# export KPOW_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# export FLEX_SUFFIX="-ce" # Community
# Licenses:
# export KPOW_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
# export FLEX_LICENSE=<path-to-license-file>
docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml up -d \
&& docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml up -d
Deploy source connector
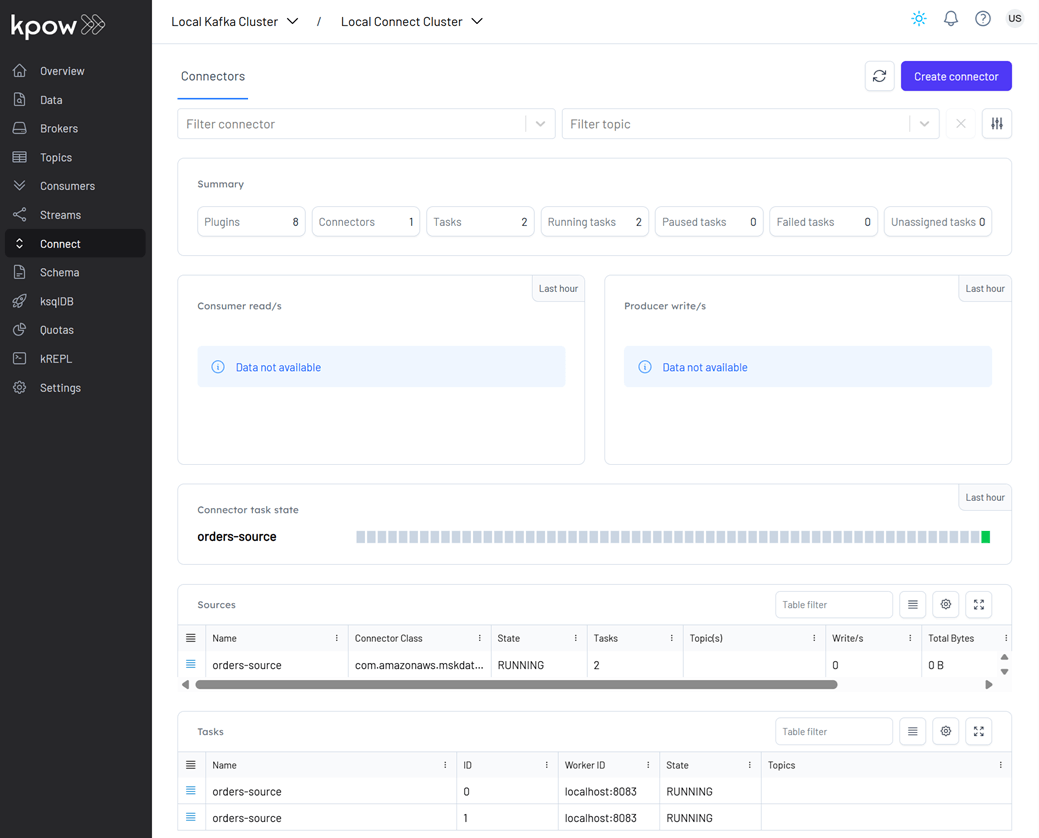
We will create a source connector that generates fake order records to a Kafka topic (orders). See the Kafka Connect via Kpow UI and API lab for details about how to create the connector.
Once deployed, we can check the connector and its tasks in Kpow.
Flink SQL Runner
We use a custom Python client (flink_sql_runner.py) to interact with the Flink SQL Gateway REST API.
The script performs:
- Session creation
- Kafka table registration (with Avro & Schema Registry)
- Tumbling window aggregation query
- Real-time result fetching
- Cleanup on exit or
Ctrl+C
The source table is defined using the Kafka SQL connector, enabling Flink to consume Avro-encoded messages from the orders Kafka topic. To support time-based processing and windowed aggregations, an event-time watermark is introduced on bid_time using WATERMARK FOR bid_time AS bid_time - INTERVAL '5' SECOND. This watermark allows Flink to track event time progress and handle out-of-order events, which is required for time-based operations such as windowed aggregations or joins.
📌 Watermarking is applied on the bid_time column to enable proper event-time windowing.
Source Table DDL
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id STRING,
item STRING,
price STRING,
supplier STRING,
bid_time TIMESTAMP(3),
WATERMARK FOR bid_time AS bid_time - INTERVAL '5' SECOND
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 'orders',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = 'kafka-1:19092',
'format' = 'avro-confluent',
'avro-confluent.schema-registry.url' = 'http://schema:8081',
'avro-confluent.basic-auth.credentials-source' = 'USER_INFO',
'avro-confluent.basic-auth.user-info' = 'admin:admin',
'avro-confluent.schema-registry.subject' = 'orders-value',
'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset'
);
Aggregation Query
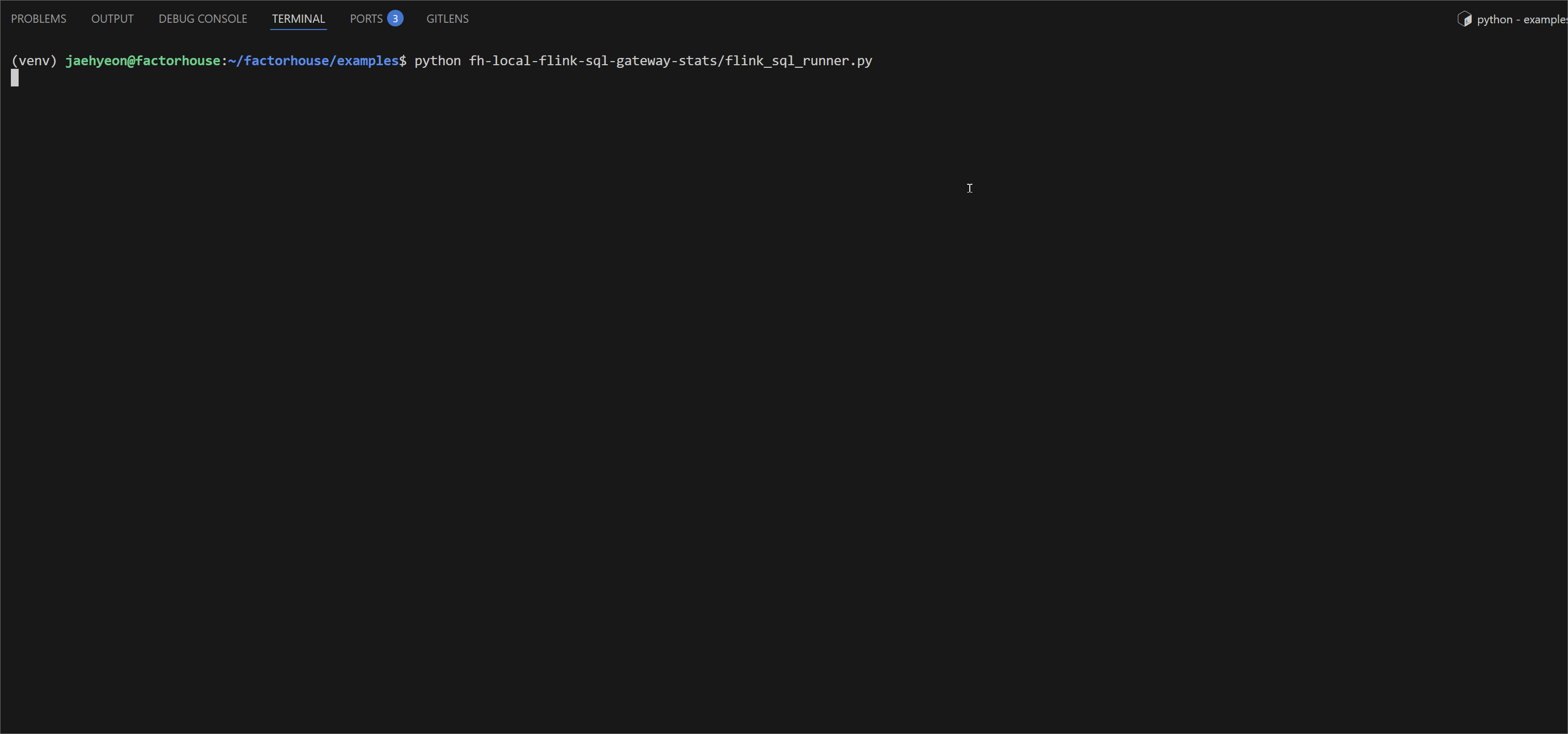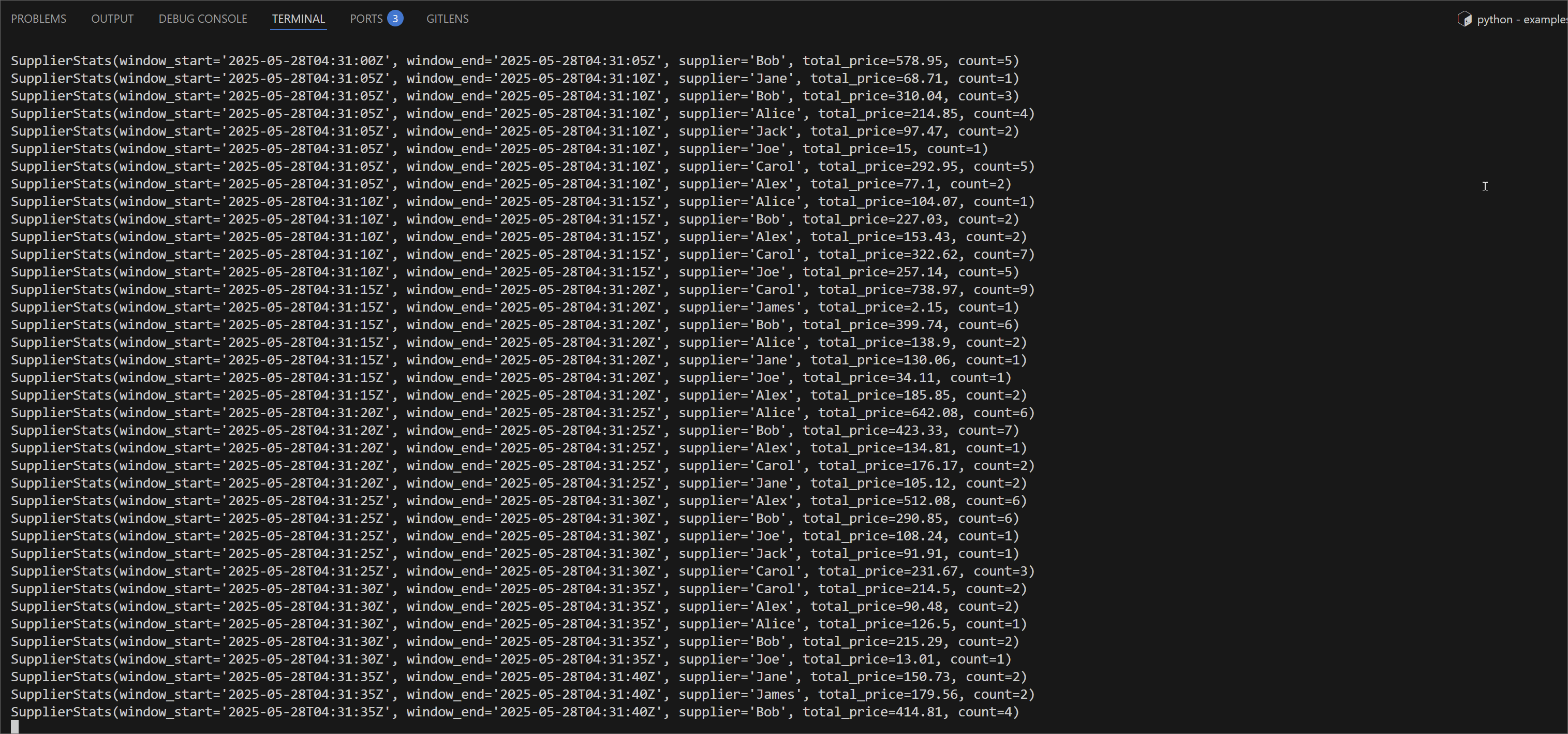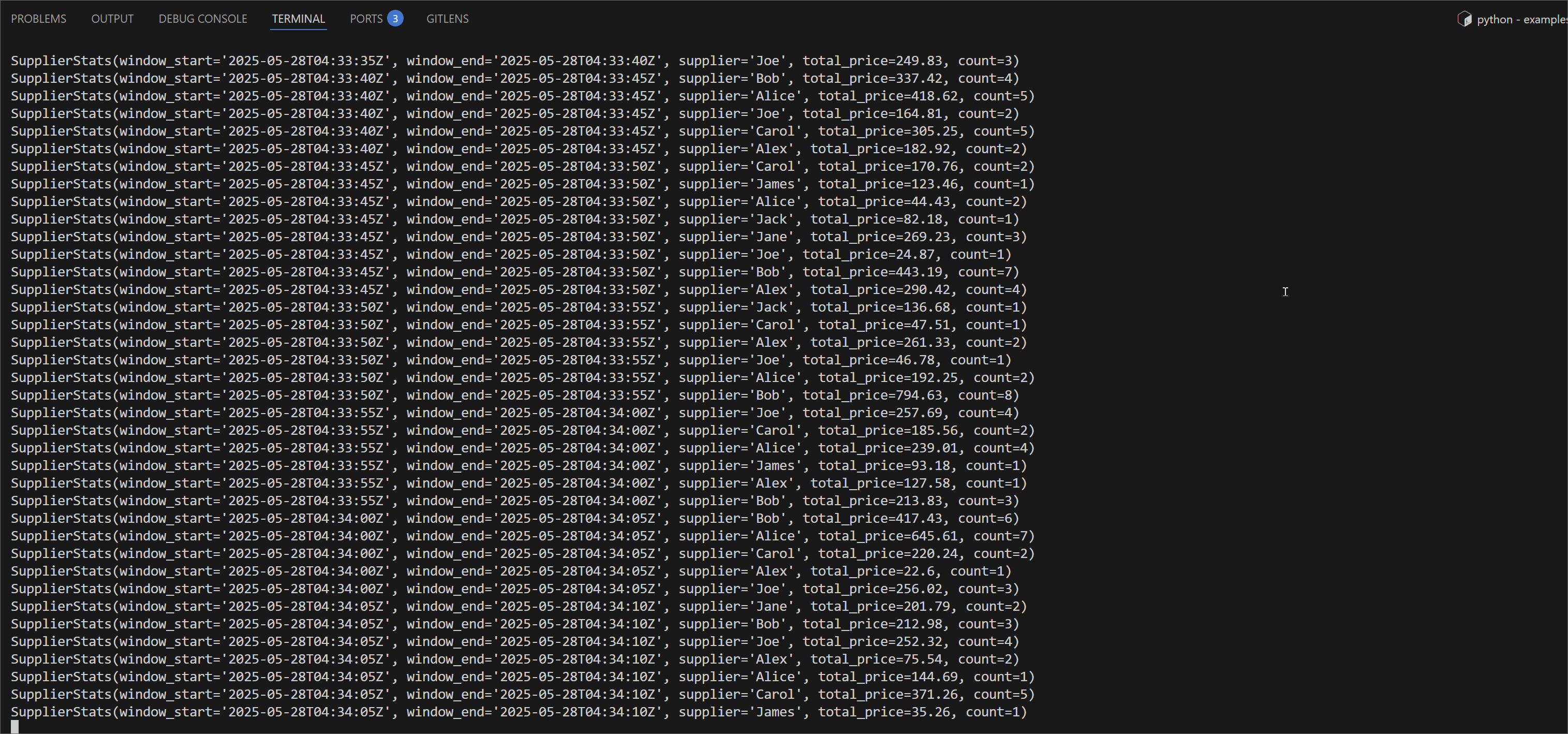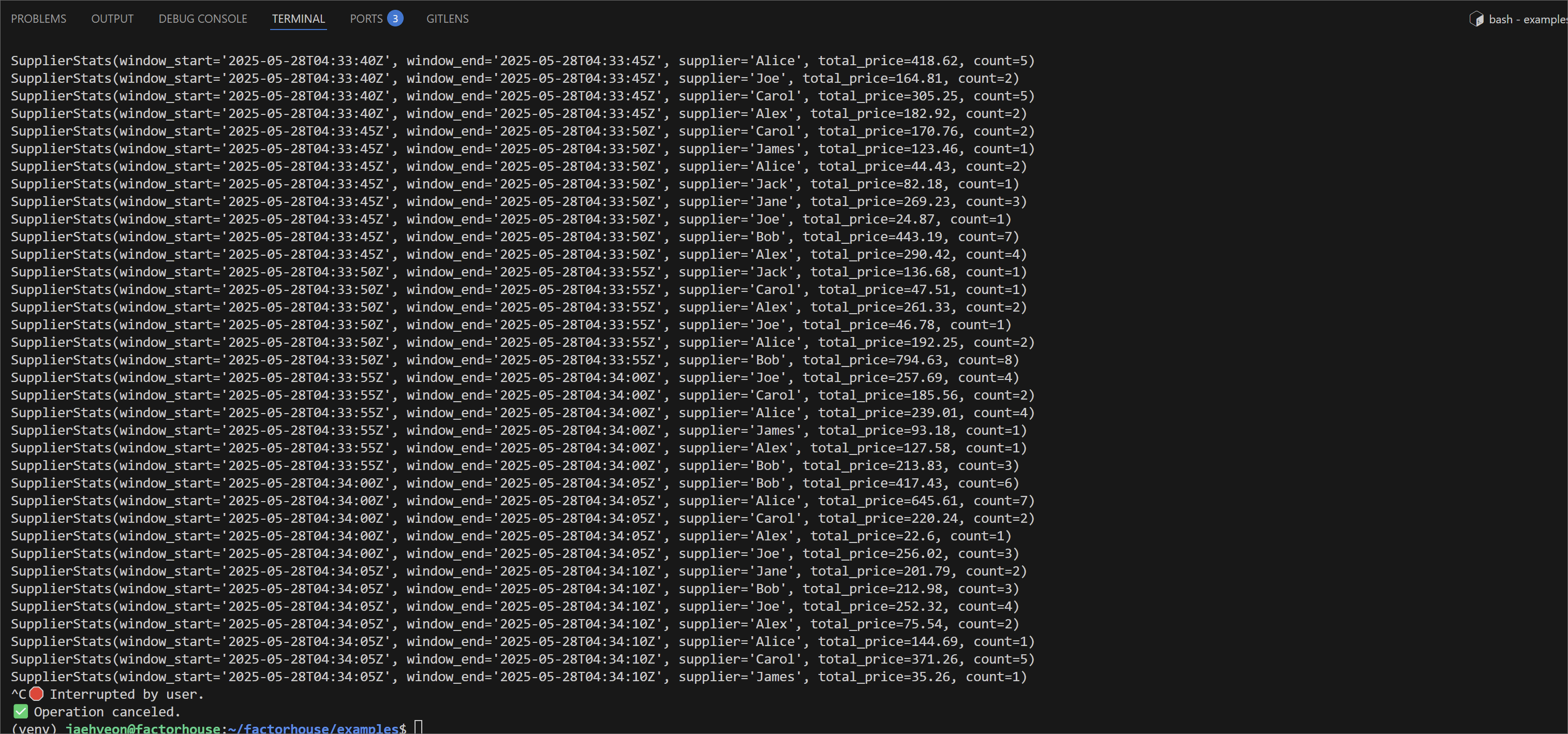
This aggregates data per supplier in fixed 5-second windows, computing:
- Window start/end (UTC)
- Total price
- Bid count
INSERT INTO supplier_stats
SELECT
DATE_FORMAT(window_start, 'yyyy-MM-dd''T''HH:mm:ss''Z''') AS window_start,
DATE_FORMAT(window_end, 'yyyy-MM-dd''T''HH:mm:ss''Z''') AS window_end,
supplier,
SUM(CAST(price AS DECIMAL(10, 2))) AS total_price,
count(*) AS `count`
FROM TABLE(
TUMBLE(TABLE orders, DESCRIPTOR(bid_time), INTERVAL '5' SECOND))
GROUP BY window_start, window_end, supplier;
Execute Flink SQL Runner
From the project root:
# Create and activate a virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
# Install required Python packages
pip install -r fh-local-labs/lab-11/requirements.txt
# Run the Flink SQL runner application
python fh-local-labs/lab-11/flink_sql_runner.py
We'll see streaming results in the terminal:
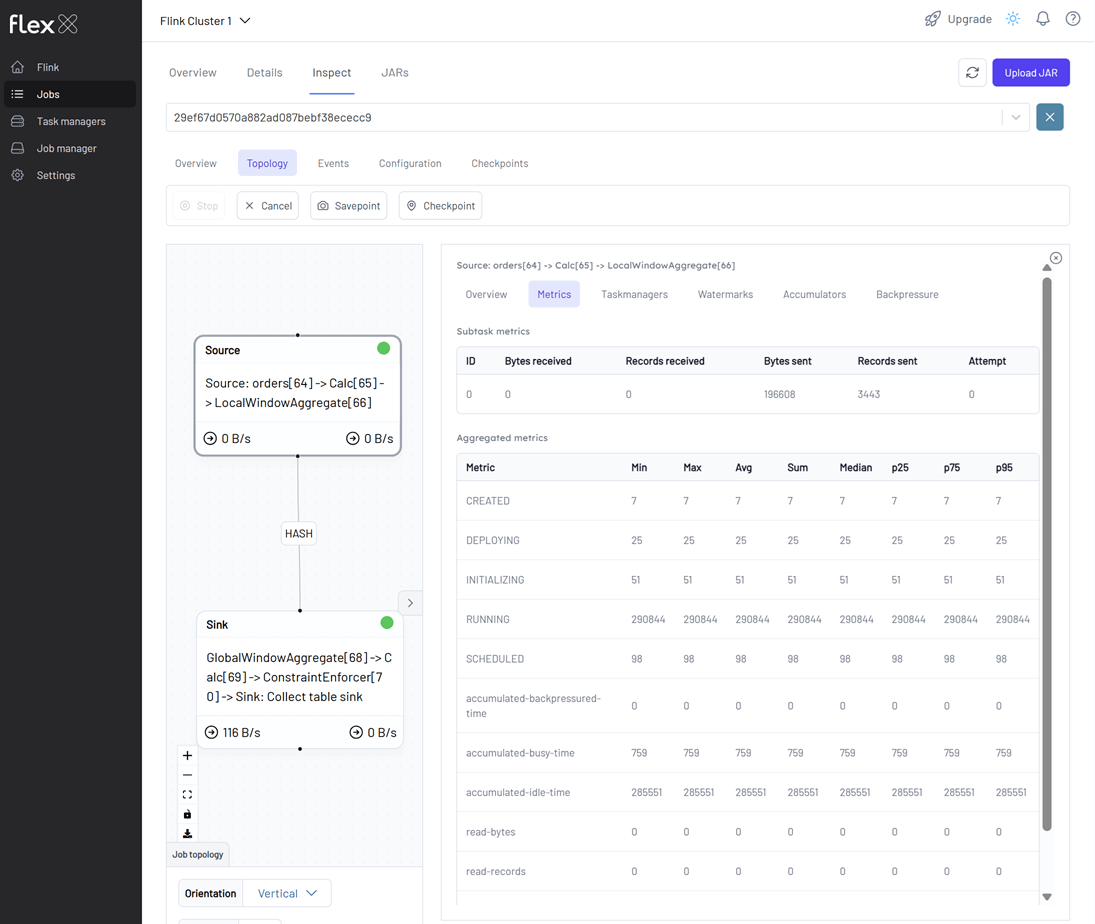
We can monitor the Flink job via the Flink UI (http://localhost:8082) or Flex (http://localhost:3001). The screenshot below shows the job's logical plan as visualized in Flex.
Shutdown environments
Finally, stop and remove the Docker containers.
If you're not already in the project root directory, navigate there first. Then, stop and remove the Docker containers by running:
# Stops the containers and unsets environment variables
docker compose -p flex -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-flex.yml down \
&& docker compose -p kpow -f ./factorhouse-local/compose-kpow.yml down
unset KPOW_SUFFIX FLEX_SUFFIX KPOW_LICENSE FLEX_LICENSE